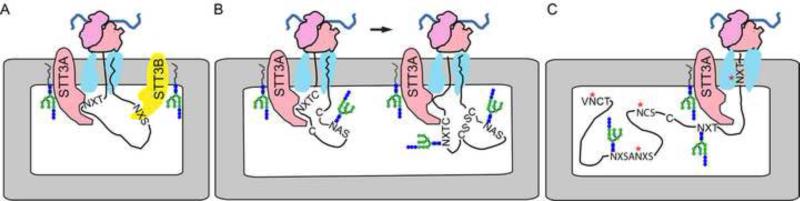
Fig. 1.
Cotranslational glycosylation of proteins by the STT3A complex. (A) The STT3A complex is associated with the protein translocation channel and scans the growing polypeptide for glycosylation acceptor sites. The STT3B complex occupies a more distal position, but is able to modify skipped glycosylation sites by a cotranslational or posttranslocational mechanism. (B) Cotranslational scanning of the nascent polypeptide allows efficient glycosylation of acceptor sites in cysteine-rich proteins before disulfide bond formation stabilizes protein tertiary structure. (C) Examples of N-terminal, internal and extreme C-terminal acceptor sites (red asterisks) that have been skipped by the STT3A complex.