FIG 1.
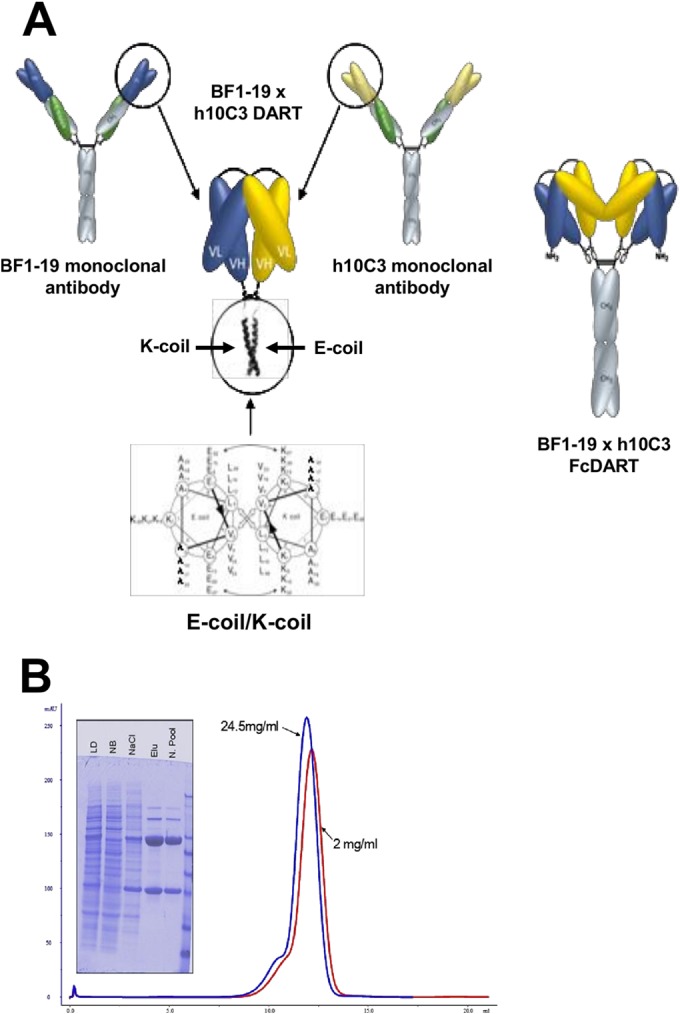
Structure and characterization of FcDART. (A) The VH and VL segments of monoclonal antibodies h10C3 and BF1-19 (yellow and blue, respectively) were combined into a single bispecific Fc fusion protein, FcDART. Shown in detail are the heterodimerization domains of FcDART, which were appended to the C terminus of each chain to promote heterodimeric assembly. These domains consisted of coiled coil-forming sequences where the hydrophobic core of the coiled coil interface is flanked by opposite charges (an E negative charge on one coil [E-coil] and a K positive charge on the other [K-coil]), which is believed to favor heterodimerization by repelling a homotypic association and preventing the initiation of zippering of the hydrophobic core. An Fc domain was also added to the C terminus of the coil with an E negative charge, causing two DART units to dimerize and form a tetravalent bispecific structure. (B) Characterization of FcDART by denaturing, reducing SDS-PAGE and size exclusion chromatography analysis. LD, load fraction on the protein A column; NB, nonbound fraction on the protein A column; NaCl, high-salt wash; Elu, material that eluted at low pH; N. Pool, material that eluted at low pH and that was neutralized. The size exclusion chromatography profiles of purified material at two concentrations (red, 2 mg/ml; blue, 24.5 mg/ml) show peak elution at about 12 ml. The slight difference in the peak elution volume is within the range of variability of manual loading and does not indicate a significant elution volume difference between the two samples.
