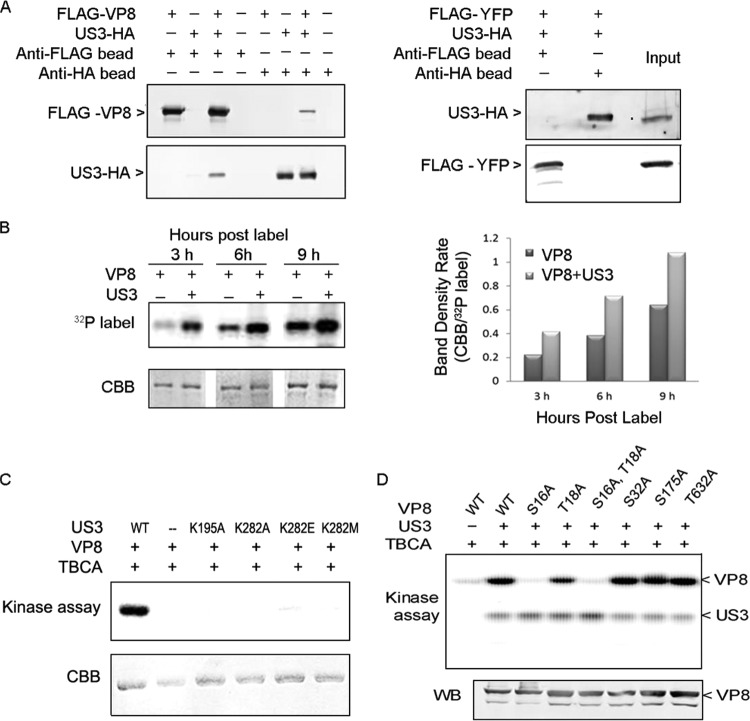
FIG 2.
VP8 is a substrate for US3, and S16 is a critical residue for phosphorylation. (A) FLAG-VP8 interacts with US3-HA. COS-7 cells were cotransfected with pFLAG-VP8 and pUS3-HA. Cell lysates were collected at 48 hpt. Protein was purified by incubating cell lysate with anti-FLAG beads or anti-HA beads for 12 h at 4°C and analyzed by Western blotting. pFLAG-YFP was used as a negative control for coimmunoprecipitation. FLAG-VP8, US3-HA, and FLAG-YFP were detected by monoclonal anti-VP8 antibody, polyclonal anti-US3 antibody, and monoclonal anti-FLAG antibody, respectively, followed by IRDye 680RD goat anti-rabbit IgG or IRDye 800CW goat anti-mouse IgG. (B) The presence of US3 increases phosphorylation of VP8 in vivo. COS-7 cells cotransfected with pFLAG-VP8 and pUS3-HA or transfected with pFLAG-VP8 were labeled with [32P]orthophosphate at 12 hpt. After a subsequent 3, 6, and 9 h of incubation, FLAG-VP8 was purified from the cell lysate by anti-FLAG beads. The samples were separated by SDS-PAGE, exposed to Imaging Screen-K, and stained with CBB. Band densities were scanned by the Quantity One program (CBB/32P-labeled band). (C) VP8 is phosphorylated by wild-type US3 but not by US3 mutants. VP8 and US3 (wild type or mutant) were analyzed by in vitro kinase assays with [λ-32P]ATP. TBCA was used to inhibit cellular kinases carried over by anti-FLAG beads and anti-HA beads during the protein purification process. Proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and exposed to Imaging Screen-K. (D) VP8 mutants were generated by replacing the serine/threonines with alanines. The VP8 mutants were analyzed by an in vitro kinase assay. Protein expression was confirmed by Western blotting with monoclonal anti-VP8 antibody and IRDye 800CW goat anti-mouse IgG.