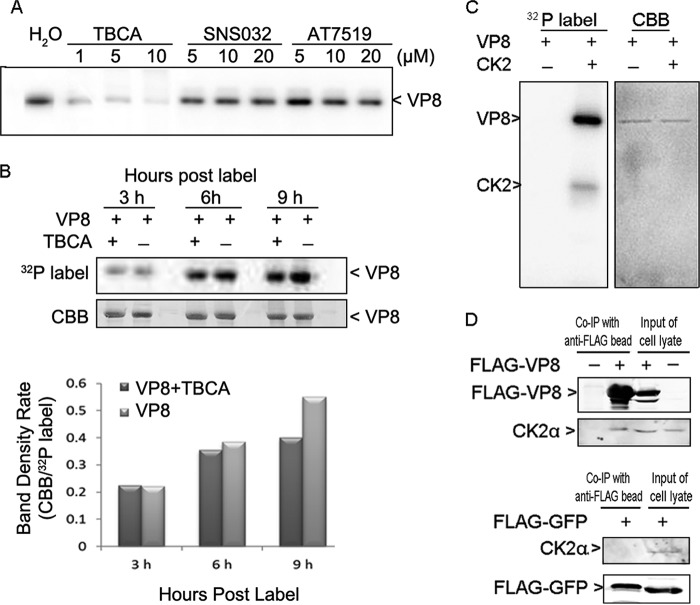
FIG 3.
VP8 is a substrate for CK2 and interacts with CK2. (A) Inhibition of VP8 phosphorylation in the in vitro kinase assay by TBCA. Different kinase inhibitors were applied to the in vitro kinase assays with VP8 and cellular kinases. (B) Reduction of VP8 phosphorylation by TBCA in pFLAG-VP8-transfected COS-7 cells. Cells were pretreated with TBCA at 80 μM for 3 h and then transfected with pFLAG-VP8. At 12 hpt, the cells were labeled with [32P]orthophosphate for 3, 6, and 9 h in the presence of TBCA. The whole-cell lysate was applied to the immunoprecipitation assay as described in the legend of Fig. 2B. (C) Phosphorylation of VP8 by CK2 and CK2α auto-phosphorylation. VP8 and CK2 were analyzed by an in vitro kinase assay. The 45-kDa protein, matching the molecular mass of CK2α, was phosphorylated. (D) Interaction of VP8 with CK2α in pFLAG-VP8-transfected COS-7 cells. Cell lysates were collected at 48 hpt and subjected to a coimmunoprecipitation (Co-IP) assay. The whole-cell lysates were analyzed to show protein expression in transfected cells. VP8, CK2α, and FLAG-YFP were detected by monoclonal anti-VP8 antibody, polyclonal anti-CK2α antibody, and monoclonal anti-FLAG antibody, respectively, followed by IRDye 680RD goat anti-rabbit IgG or IRDye 800CW goat anti-mouse IgG.