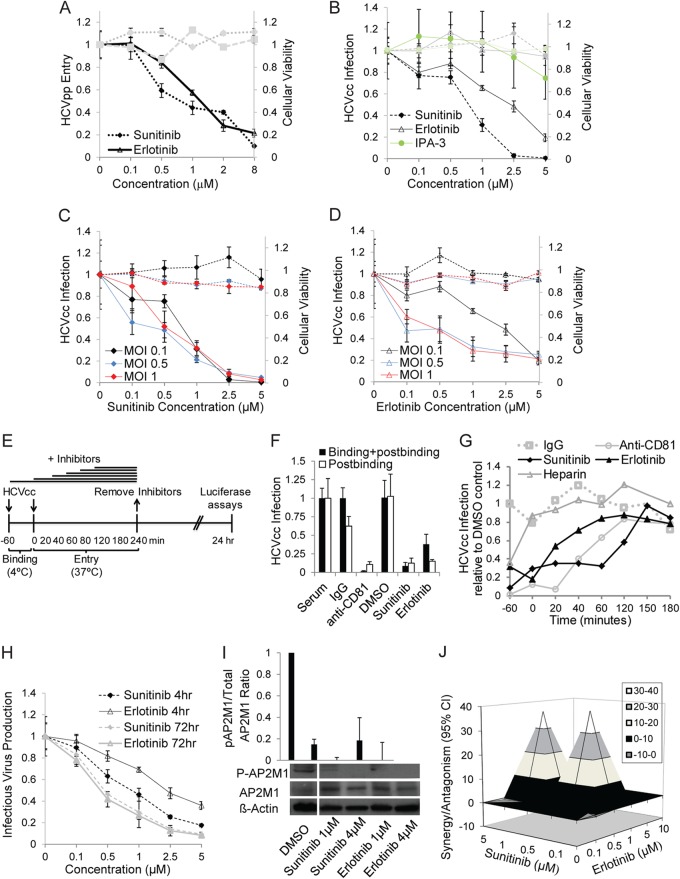
FIG 6.
Pharmacological inhibitors of AAK1 and GAK inhibit HCV entry at a postbinding step. (A and B) Huh-7.5 cells were infected with HCVpp or HCVcc for 1 h on ice, followed by a temperature shift to 37°C, a 4-h treatment with various concentrations of sunitinib, erlotinib, IPA-3, or DMSO, and medium replacement. Data represent dose-response curves of the effect of the indicated inhibitors on HCVpp entry and HCVcc infection (MOI of 0.1) by luciferase assays at 72 and 24 h postinfection, respectively. The y axes at left (black lines) represent relative luciferase values normalized to the DMSO-treated controls. These compounds had no effect on cellular viability at the concentration range used, as measured by alamarBlue-based assays. The y axes at right (gray lines) represent relative fluorescence values normalized to DMSO-treated controls. Data represent means and standard deviations (error bars) from at least three experiments in triplicates. (C and D) Dose-response curves of the effects of sunitinib and erlotinib on HCVcc infection by luciferase assays at 24 h postinfection at the indicated MOIs. (E to G) Time-of-addition experiments, depicted graphically in panel E, were performed by incubation of cells with HCVcc (MOI of 0.2) for 1 h at 4°C and transfer to 37°C. Serum, IgG, anti-CD81 antibody, DMSO, erlotinib, sunitinib, or heparin was added either during the binding step or at various time points after the temperature switch. Data are relative luciferase values normalized to the value of the DMSO control after inhibition of binding and postbinding steps (F) and the time course of HCVcc infection following inhibition with the indicated compounds (G). (H) Supernatants collected from Huh-7.5 cells following HCVcc infection and either a single 4-h or 72-h daily treatment were used to inoculate naive cells. Data represent dose-response curves of the drugs' effects on infectious virus production measured by luciferase assay. (I) Huh-7.5 cells were infected with HCVcc, treated with sunitinib and erlotinib at the indicated concentrations or with DMSO in the presence of calyculin A (an AP2M1 dephosphorylation inhibitor [117]) and subsequently lysed. The effect of the inhibitors on AP2M1 phosphorylation was measured by Western analysis in these cell lysates. A representative membrane blotted with anti-phospho-AP2M1 (p-AP2M1), anti-AP2M1, and anti-actin antibodies and quantitative analysis from three experiments are shown. The y axis represents the relative p-AP2M1/total AP2M1 protein ratio normalized to the value of the DMSO controls. (J) Combinations of sunitinib and erlotinib at the indicated concentrations were used to treat HCVcc-infected cells. Data represent the differential surface analysis at the 95% confidence level (CI) (MacSynergy II). Peaks above the theoretical additive plane indicate synergy, whereas depressions below it indicate antagonism. The level of synergy or antagonism is as indicated by the color code on the figure. Results of a representative experiment (out of three) are shown.