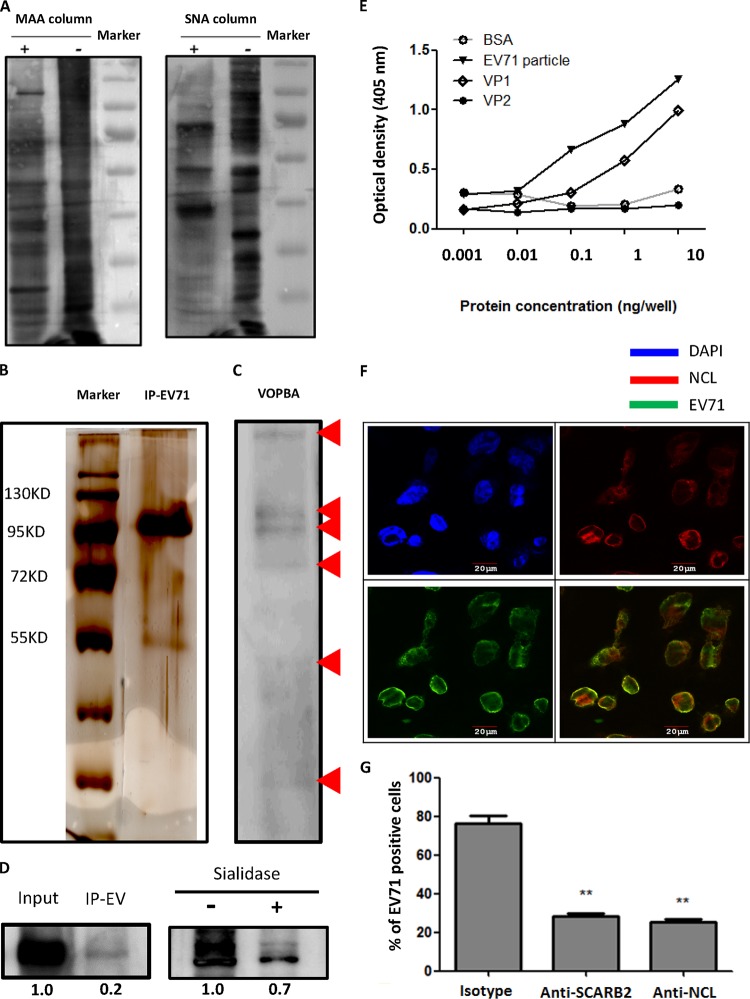
FIG 1.
Identification and characterization of EV71-interacting glycoproteins. (A) Membrane proteins column purified with (+) or without (−) MAA or SNA were separated by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with HRP-conjugated MAA and HRP-conjugated SNA lectins. (B) The silver staining of EV71-immunoprecipitated desialylated membrane proteins is shown. (C) The VOPBA of desialylated membrane proteins binding to EV71 particles is shown. Red arrows indicate the bands observed on VOPBA. (D) RD cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with EV71 particles (IP EV) and immunoblotted with antinucleolin (anti-NCL) antibody and HRP-conjugated secondary antibody (left panel). Sialylated membrane proteins, with or without sialidase treatment, were immunoprecipitated with EV71 particles and immunoblotted with anti-NCL antibody and HRP-conjugated secondary antibody (right panel). (E) The binding of serially diluted BSA, EV71 particles, VP1, and VP2 recombinant proteins (from 1 pg/well to 10 ng/well) with pure NCL protein was determined by ELISA. (F) The colocalization (yellow) of EV71 (green) with NCL (red) was observed by confocal microscopy in infected RD cells. Nuclei were stained in blue by DAPI. (G) Anti-SCARB2 or anti-NCL antibody (50 μg/ml) significantly reduced the binding of EV71 to RD cells as determined by flow cytometry. The data are representative of the means ± standard deviations (error bars) of ≥3 samples per group (**, P < 0.01).