FIG 1.
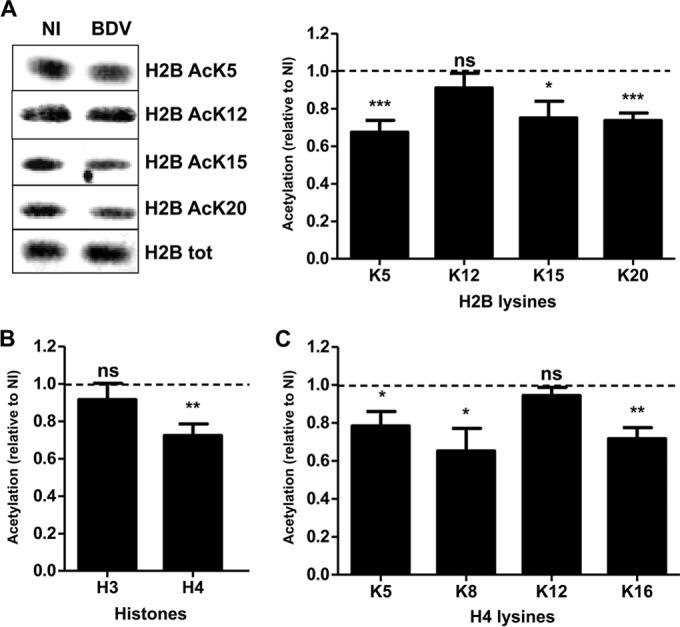
BDV infection decreases histone acetylation levels in primary neuronal cultures. (A) Western blot analysis of H2B acetylation levels. (Left panel) Histone fractions were prepared from parallel noninfected (NI) or infected (BDV) neuronal cultures and analyzed by Western blotting with the indicated antibodies. Total (tot) H2B levels were assessed for each sample and used to normalize acetylation signals. (Right panel) Quantification of H2B acetylation. Acetylation values (normalized for total H2B) obtained for infected neurons were normalized to the values obtained for noninfected neurons, which were set to 1 and which are represented by the dashed lines on the graphs. Data are expressed as means ± SEM of the results from at least nine independent sets of neuronal cultures. *, P ≤ 0.05; **, P ≤ 0.01; ***, P ≤ 0.001; ns = nonsignificant (by paired t test). (B) Analysis of global H3 and H4 acetylation by Western blotting, done as described for panel A. (C) Analysis of acetylation on each H4 lysine residue by Western blotting, done as described for panel A.
