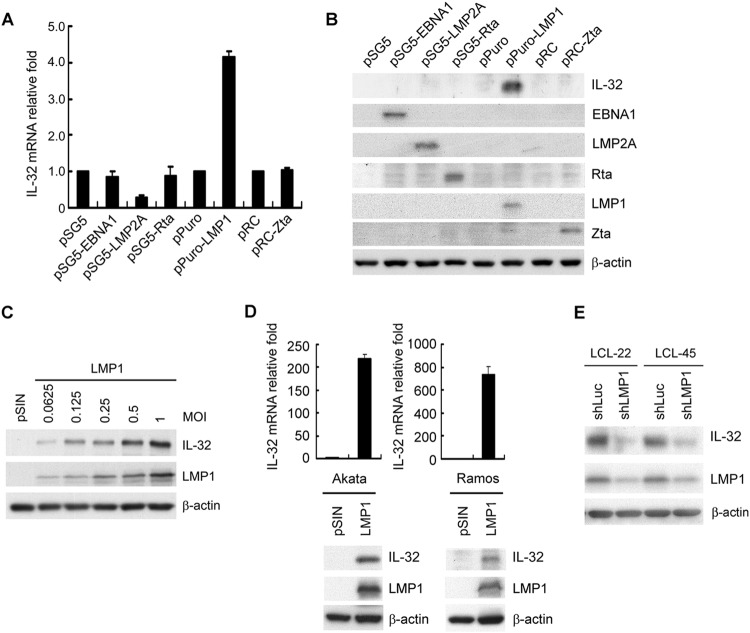
FIG 2.
EBV LMP1 induces IL-32 expression. (A and B) EBV-negative Akata cells were electroporated with the plasmids indicated. RNA and proteins were harvested from each transfectant at 72 h posttransfection. (A) IL-32 transcripts were measured by RT-qPCR, and the relative fold was normalized to the amounts of IL-32 transcripts from vector control cells. (B) Expression of IL-32, EBNA1, LMP2A, Rta, LMP1, Zta, and β-actin was detected by Western blotting. β-Actin served as the internal control. (C) Akata cells were infected with the pSIN vector- or LMP1-expressing lentiviruses at the indicated MOI for 5 days. Expression of IL-32, LMP1, and β-actin was detected by Western blotting. β-Actin served as the internal control. (D) Akata and Ramos cells were infected with the pSIN vector- or LMP1-expressing lentiviruses at an MOI of 4 for 5 days. IL-32 transcripts were measured by RT-qPCR, and the relative fold was normalized to the amounts of IL-32 transcripts from vector control cells (upper portion). Expression of IL-32, LMP1, and β-actin was detected by Western blotting. β-Actin served as the internal control (lower portion). (E) LCLs were infected with shLuciferase (shLuc) or shLMP1 lentiviruses at an MOI of 2 for 5 days. Expression of IL-32, LMP1, and β-actin was measured by Western blotting. β-Actin served as the internal control.