FIG 2.
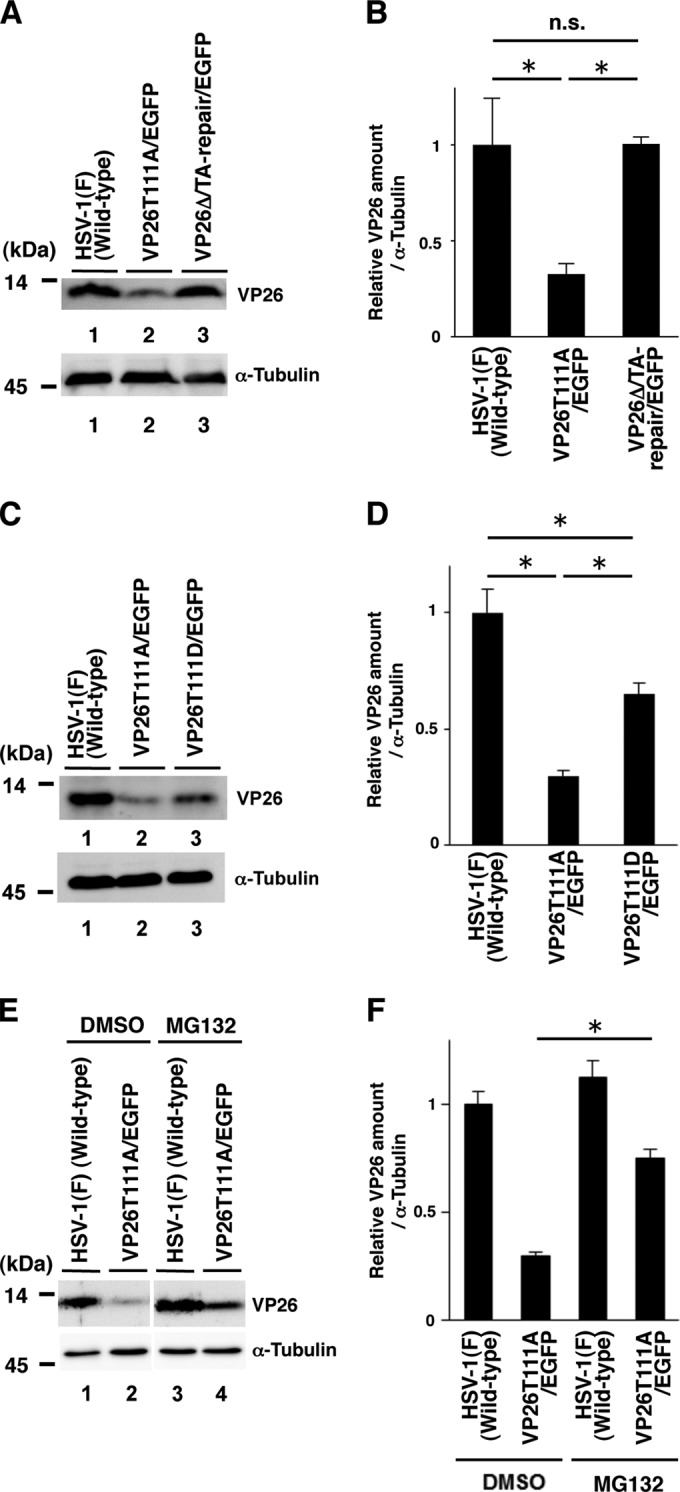
Effects of the mutations in VP26 on its expression in SK-N-SH cells. (A and C) SK-N-SH cells infected with each of the indicated viruses at an MOI of 5 were harvested 24 h postinfection and analyzed by immunoblotting with an antibody to VP26 or α-tubulin. (B and D) The amount of VP26 in the SK-N-SH cells shown in panels A and C (top) relative to those of α-tubulin shown in panels A and C (bottom). Each value is the mean ± standard error of triplicate experiments and is expressed relative to the mean value of wild-type HSV-1(F)-infected SK-N-SH cells, which was normalized to 1. Asterisks indicate significant differences: *, P < 0.05 (by analysis of variance and Tukey's test); n.s., not significant. (E) SK-N-SH cells infected with each of the indicated viruses at an MOI of 5 were treated with DMSO or 20 μM MG132 6 h postinfection, and infection proceeded for an additional 18 h in the presence of DMSO or MG132. Infected cells were then harvested and analyzed by immunoblotting with an antibody to VP26 or α-tubulin. (F) Amount of VP26 in the SK-N-SH cells shown in top blot in panel E relative to that of α-tubulin, shown in the bottom blot in panel E. Each value is the mean ± standard error of triplicate experiments and is expressed relative to the mean value of wild-type HSV-1(F)-infected SK-N-SH cells treated with DMSO, which was normalized to 1. Asterisks indicate significant differences: *, P < 0.05 (by two-tailed Student's t test).
