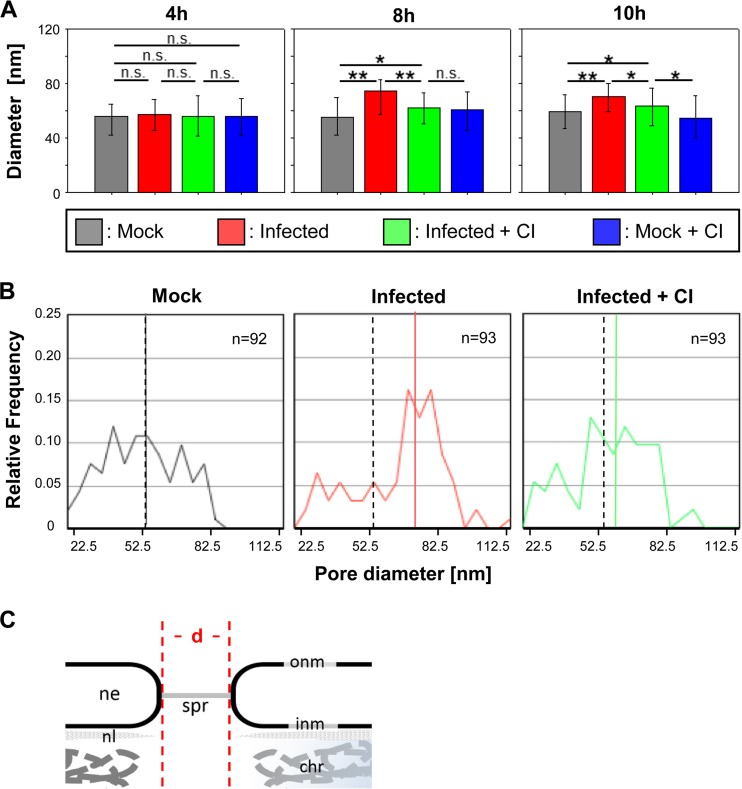
FIG 6.
Increase of nuclear pore diameters in IV-infected cells. (A) Diameters of nuclear pores (median values) in MDCK-II cells under different experimental conditions (mock treatment, FPV infection, FPV infection plus caspase 3/7 inhibition [CI], and mock treatment plus CI) and at different time points p.i. Error bars indicate interquartile ranges. Significance levels are indicated (n.s., no significant difference; *, P ≤ 0.05; **, P ≤ 0.001). (B) Distribution of nuclear pore diameters in FPV-infected MDCK-II cells at 8 h p.i. after mock treatment (left), after infection (middle), and after infection plus CI treatment (right). The colored lines represent the median value for each sample. As a reference, the median value of the control (mock-treated) group is also indicated for the two other groups by a dashed line. (C) Panel showing the main structural elements of the NPC seen in the electron microscopy (em) images and indication of how the diameters (d) of the pores were measured. chr, chromatin; ne, nuclear envelope; onm and inm, outer and inner nuclear membranes; spr, spoke ring; nl, nuclear lamina.