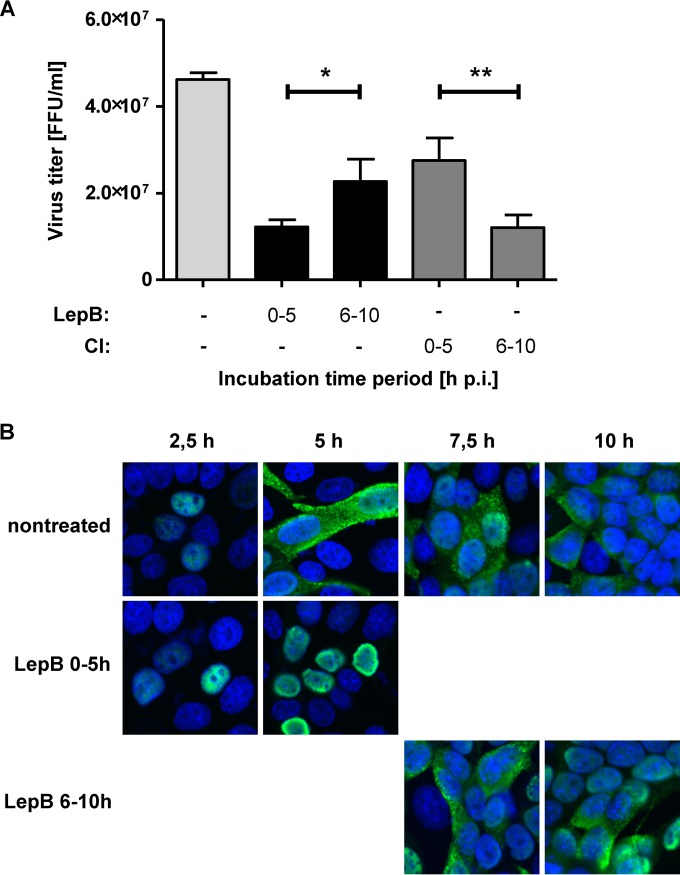
FIG 8.
Relevance of Crm1-dependent transport pathways for nuclear RNP export at different time points in the viral replication cycle. (A) MDCK-II cells were infected with FPV (MOI = 1), and inhibitors of Crm1 (Leptomycin B [LepB], black bars) or caspase 3/7 (CI, gray bars) were added for different time periods p.i. as indicated. Virus titers in cell culture supernatants collected at 10 h p.i. were determined. Experiments were done in triplicate, and standard deviations are indicated. (*, P = 0.029; **, P = 0.004). FFU, focus-forming units. (B) MDCK-II cells were infected with FPV (MOI = 0.5). LepB was included from 0 to 5 h or from 6 to 10 h p.i. as indicated. Intracellular RNP localization was detected by confocal laser scanning microscopy using a NP-specific MAb (green) at the indicated time points p.i. DNA was stained with DAPI (blue).