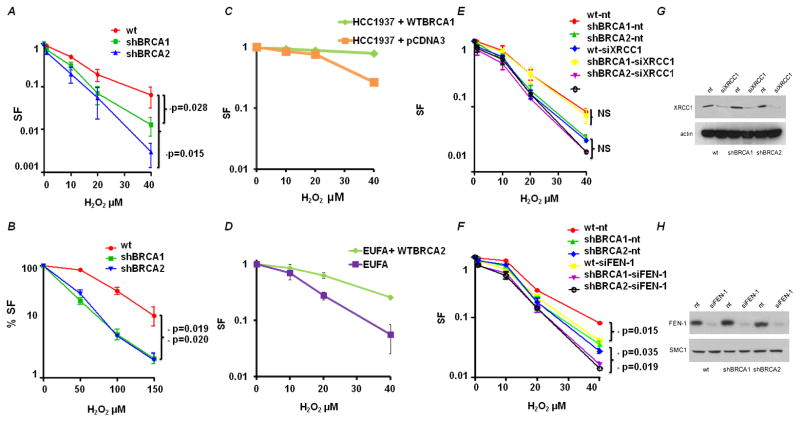
Figure 2. BRCA1- and BRCA2-deficient cells are sensitive to H2O2.
(A) Clonogenic survival of BRCA-deficient cells after exposure to H2O2. Data shown are the mean and SE of the mean from three independent experiments. The survival of BRCA1 and BRCA2 deficient cells relative to wild type MCF-7 at 40μM was compared for statistical significance. (B) MTS assay of BRCA-deficient cells after exposure to H2O2. (C) Clonogenic survival of BRCA1-deficient cell line – HCC1937 containing pcDNA3 empty vector and HCC137 complemented with a full-length wtBRCA1 construct after exposure to H2O2. Data shown are the mean and SE from three independent experiments. (D) Clonogenic survival of BRCA2-deficient cell line – EUFA and EUFA complemented with a full-length wtBRCA2 construct after exposure to H2O2. Data shown are the mean and SE from three independent experiments. (E) XRCC1-depletion in wild type and BRCA-deficient cells. Cells were harvested 48h after siXRCC1 or control siRNA (nt) nucleofection and cell lysates were immuno-blotted for XRCC1. Clonogenic survival of wild type and BRCA deficient cells nucleotransfected with siXRCC1 or control siRNA (nt) after exposure to H2O2 as in A. (F) The effect of FEN1-depletion as in E. (G) Representative immunoblots confirming XRCC1 depletion in BRCA1 and BRCA2 deficient cells. (H) Representative immunoblots confirming FEN1 depletion in BRCA1 and BRCA2 deficient cells. Actin was used as loading control. Cell lines were nucleotransfected with FEN1/XRRC1 siRNA and post 48 hrs from transfection, cells were harvested for immunoblotting.