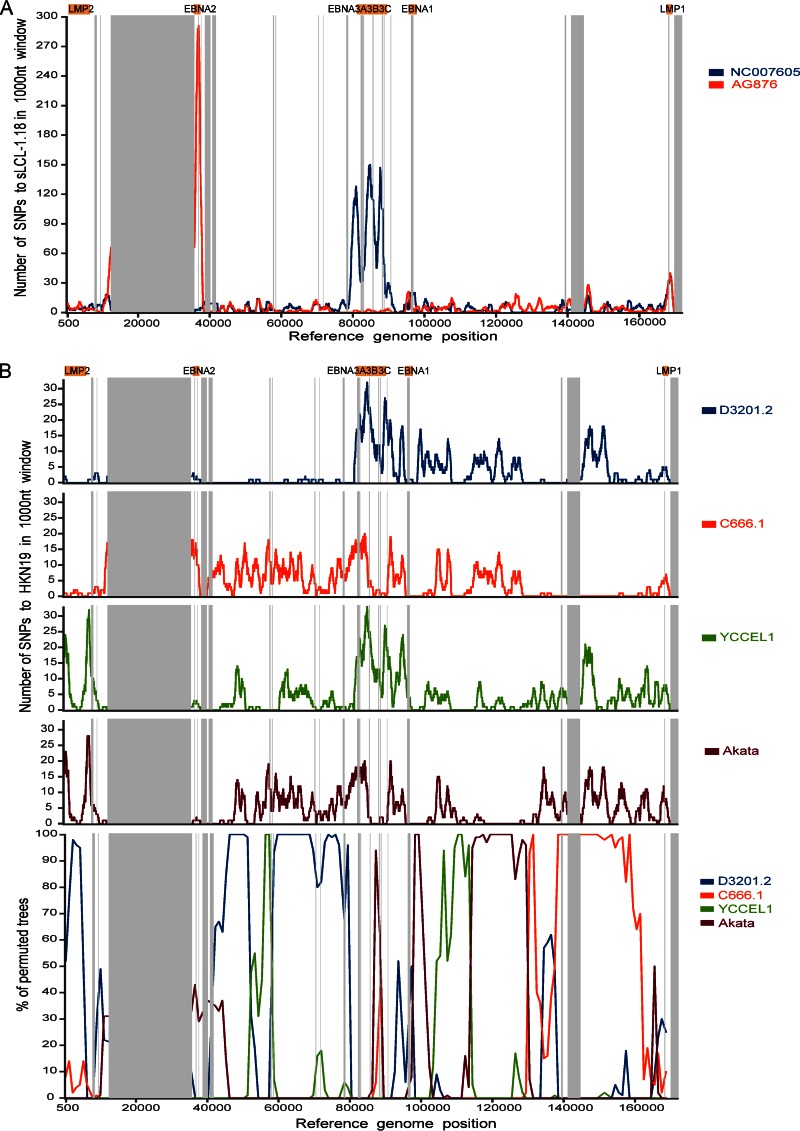
FIG 6.
Recombination between different EBV strains. (A) Intertypic recombination between type 1 and type 2 EBV strains. Diversity plots show the number of SNPs per 1,000-nt sliding window comparing EBV strain sLCL-1.18 with the type 1 reference genome (NC_007605; blue) and the type 2 reference genome (AG876; red). Major repeat regions are masked out (vertical gray bars). The sLCL-1.18 EBV genome is highly similar to the type 1 genome in the EBNA2 region (around positions 36000 to 37000) and highly similar to type 2 in the EBNA3s region (around positions 80000 to 89000). (B) Evidence for recombination between different type 1 EBV strains. Diversity and bootscan plots comparing strain HKN19 with 4 geographically related (southeast Asian) EBV strains, with repeat regions masked out (gray bars). Diversity plots (top; number of SNPs in a 1,000-nt sliding window) show high levels of similarity (few SNPs) between HKN19 and strain D3201.2 until approximately position 80000 and similarity to other strains in other parts of the genome. Bootscan plots (bottom) of the same strains confirm that clustering of the strains changes across the genome, indicating the presence of multiple recombination events throughout the genomes.