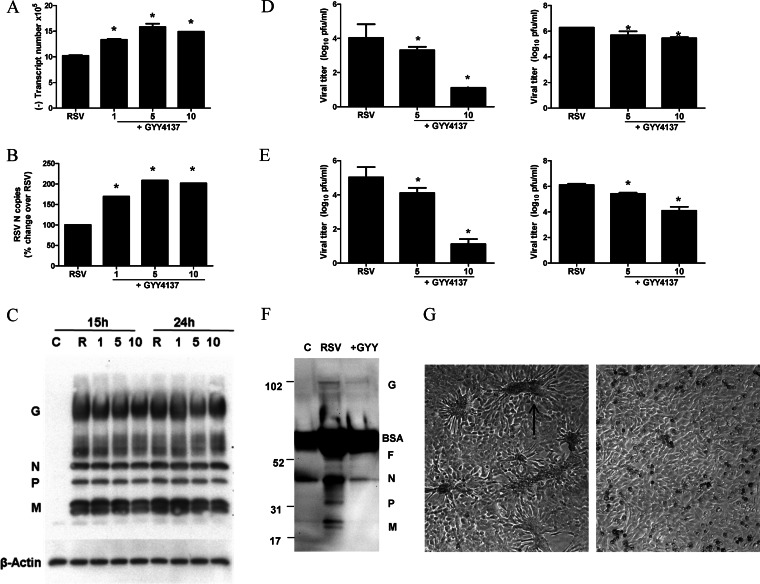
FIG 6.
Effect of H2S donor treatment on different steps of viral replication. A549 cells were infected with RSV for 1 h and then incubated in the presence or absence of GYY4137 for 24 h. (A to C) Cells were harvested to prepare either total RNA to measure viral genome copy numbers (A) or RSV N gene copy numbers (B) by qRT-PCR or total cell lysates to measure viral protein expression by Western blotting (C). The membrane was stripped and reprobed with β-actin as a control for equal loading of the samples. Data are representative of data from three independent experiments with similar results. (D) A549 cells were infected with RSV for 1 h and then incubated in the presence or absence of GYY4137 at 5 and 10 mM for 24 h. Cell supernatants (left) and cell pellets (right) were harvested separately to determine viral titers by a plaque assay. Results are expressed as means ± standard errors and are representative of data from three independent experiments run in triplicate. *, P < 0.05 compared to untreated RSV-infected cells. (E) HEp-2 cells were infected with RSV at an MOI of 0.01 in the presence or absence of GYY4137 at 5 and 10 mM for 48 h. Cell supernatants (left) and cell pellets (right) were harvested separately to determine viral titers by a plaque assay. Results are expressed as means ± standard errors and are representative of two independent experiments run in triplicate. *, P < 0.05 compared to untreated RSV-infected cells. (F) A549 cells were infected with RSV for 1 h and then incubated in the presence or absence of GYY4137 for 24 h. Cell supernatants were harvested to measure viral protein expression by Western blotting. Data are representative of data from two independent experiments with similar results. (G) Light microscopy photograph (magnification, ×20) of HEp-2 cells infected with RSV at an MOI of 0.01 for 48 h in the presence (right) or absence (left) of GYY4137 at 10 mM. The arrow indicates one of the many syncytia present in the cell monolayer as a result of viral infection.