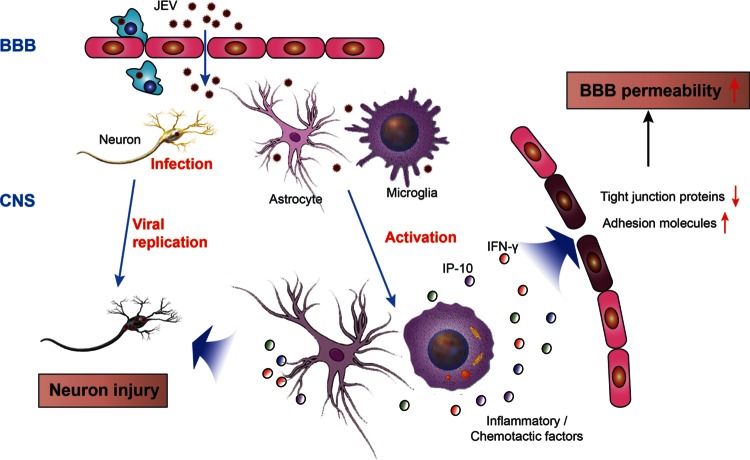
FIG 9.
Schematic representation of possible mechanisms regulating BBB permeability during JEV infection. During infection, JEV particles penetrate the BBB from the periphery into the CNS without changing BBB permeability. Neurons are vulnerable to JEV infection. Once neurons are infected, the virus begins multiplying and replicating in neurons, which causes the first round of neuronal injury accompanied by the production of cytokines or chemokines. These cytokines/chemokines activate microglia and astrocytes, which in turn stimulates more production of proinflammatory cytokines/chemokines and contributes to further neuronal injury. Cytokines and chemokines can activate immune cells inside the brain that initiate and/or potentiate BBB dysfunction and alter the architecture of tight junctions and adhesion molecules on BBB. Furthermore, transendothelial migration of leukocytes causes acute neuronal tissue damage. Consequently, BBB permeability increases.