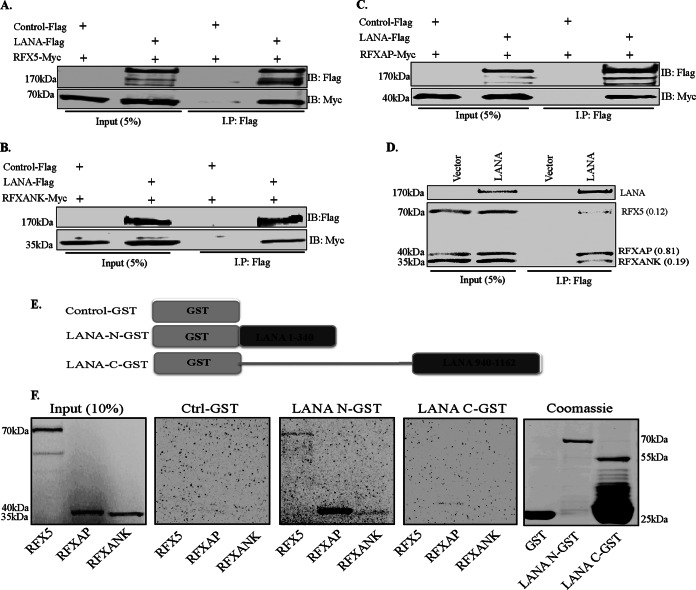
FIG 2.
LANA does not require other KSHV factors to associate with the components of the RFX complex. (A to C) Assays of protein-protein interactions of LANA with all three components of the RFX complex were performed with HEK293T cells by transiently cotransfecting cells with Flag-tagged wild-type LANA and Myc-tagged RFX5 (A), Myc-tagged RFXANK (B), or Myc-tagged RFXAP (C). The pA3F empty vector was used as a control. The cells were lysed 48 h after transfection, and LANA was immunoprecipitated by using anti-Flag antibody, followed by immunodetection with anti-Flag and anti-Myc antibodies. Overexpressed LANA efficiently coimmunoprecipitated RFX5, RFXAP, and RFXANK. (D) In vitro-translated full-length LANA-Flag protein was combined with in vitro-translated RFX5-Myc, RFXAP-Myc, and RFXANK-Myc and rotated overnight at 4°C after preclearing with protein A and G beads. LANA was immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag antibody, and the bound complexes were resolved on SDS-PAGE gels, followed by autoradiography to detect the coimmunoprecipitated proteins. Relative binding values (shown in parentheses) of RFX components were determined by taking the respective inputs as 1. (E) Schematic of LANA domains fused with GST used in pulldown assays. (F) GST pulldown assay showing binding of amino- and carboxy-terminal domains of LANA with the components of the RFX complex. Full-length in vitro-translated RFX5, RFXAP, and RFXANK proteins were rotated with either GST alone (Ctrl), LANA-N–GST, or LANA-C–GST after preclearing with GST beads. The bound proteins were resolved on SDS-PAGE gels and visualized by autoradiography. Expressions of GST and the GST fusion proteins were confirmed by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie staining (right).