FIG 9.
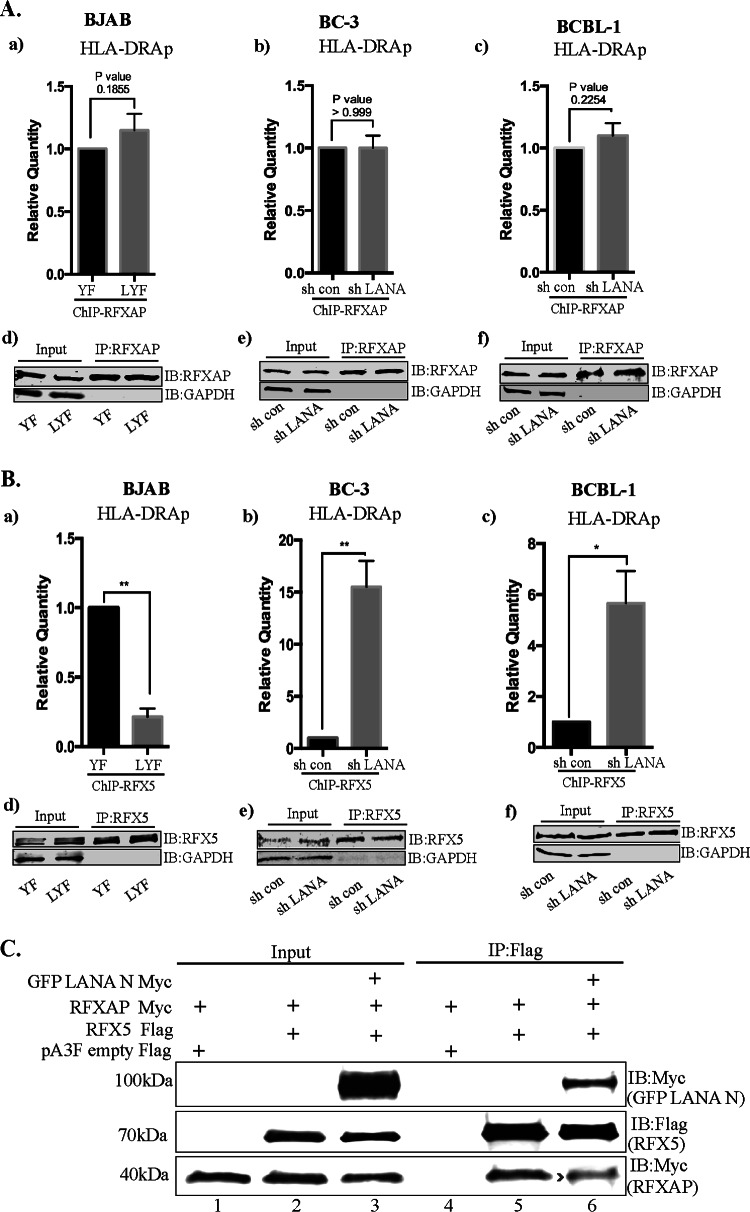
Binding of RFXAP and RFX5 to the HLA-DRA promoter in the presence of LANA. (Aa) ChIP assays coupled with qPCR analysis showing binding of RFXAP to the HLA-DRA promoter in the presence of LANA in KSHV-negative BJAB cells stably expressing LANA (LYF) or control cells with YFP expression (YFP). (b and c) LANA depletion in KSHV-infected BC3 (b) and BCBL1 (c) PEL cells by a lentiviral vector. RFXAP ChIP in BJAB-YFP and LYF cells as well as with or without LANA knockdown in BC-3 and BCBL-1 cells showed similar binding of RFXAP. The error bars represents standard deviations of the means from at least three experimental replicates. P values calculated by two-tailed t tests showed no significant difference between analyzed samples. (d to f) Efficient immunoprecipitation with anti-RFXAP antibody. (Ba) ChIP assay with anti-RFX5 antibody showing reduced copy numbers of the HLA-DRA promoter bound to RFX5 in LANA-expressing BJAB cells. (b and c) The association of RFX5 with the HLA-DRA promoter was increased when LANA was knocked down in BC-3 (b) and BCBL1 (c) cells compared to cells without LANA knockdown. The error bars represent standard deviations of the means from at least three experimental replicates. P values were calculated by two-tailed t tests. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01. (d to f) Efficient immunoprecipitation with anti-RFX5 antibody. (C) LANA-N disrupts the association of RFX5 with RFXANK. Immunoprecipitation of RFX5 (Flag tagged) in the presence of LANA-N (GFP–LANA-N–Myc) reduced the amounts of coprecipitating RFXANK compared to those in the cells without LANA-N (middle, compare lane 6 to lane 5).