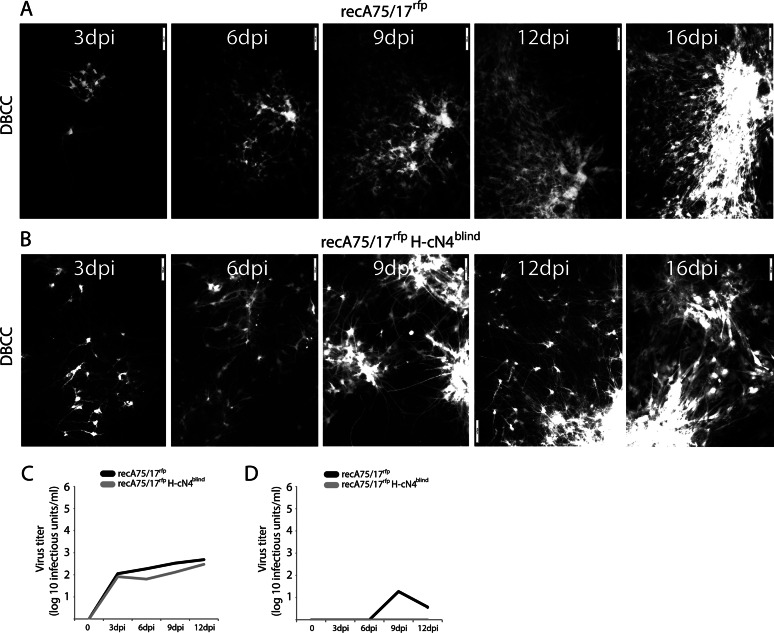
FIG 5.
Efficacy of recA75/17rfp and recA75/17rfp H-cN4blind cell-to-cell transmission in DBCCs. (A and B) Cell-to-cell spread of recA75/17rfp or recA75/17rfp H-cN4blind in DBCCs was monitored throughout a period of 16 days. Cell-to-cell transmission in living cells was performed by recording virus-induced red fluorescence emission. In both experiments representative fields of growing infected foci were captured at 3, 6, 9, 12, and 16 days postinfection (dpi) with a confocal microscope (magnification, ×100; FluoView FV1000; Olympus). (C and D) Both recA75/17rfp and recA75/17rfp H-cN4blind are defective in producing free particles in DBCCs. Growth kinetics in DBCCs of cell-associated (C) or cell-free (D) particles generated by recA75/17rfp or recA75/17rfp H-cN4blind were determined. DBCCs were infected with the both viruses at an MOI of 0.01, and particles in the supernatant or remaining bound to the cells were harvested at 0, 3, 6, 9, and 12 days postinfection. Results represent the means of three independent experiments. To determine the statistical significance of differences between the growth of the wt virus (or cN4blind mutant) in Vero cells expressing the indicated receptor compared to its growth in regular Vero cells, unpaired two-tailed t tests were performed (*, P < 0.05; **P < 0.01).