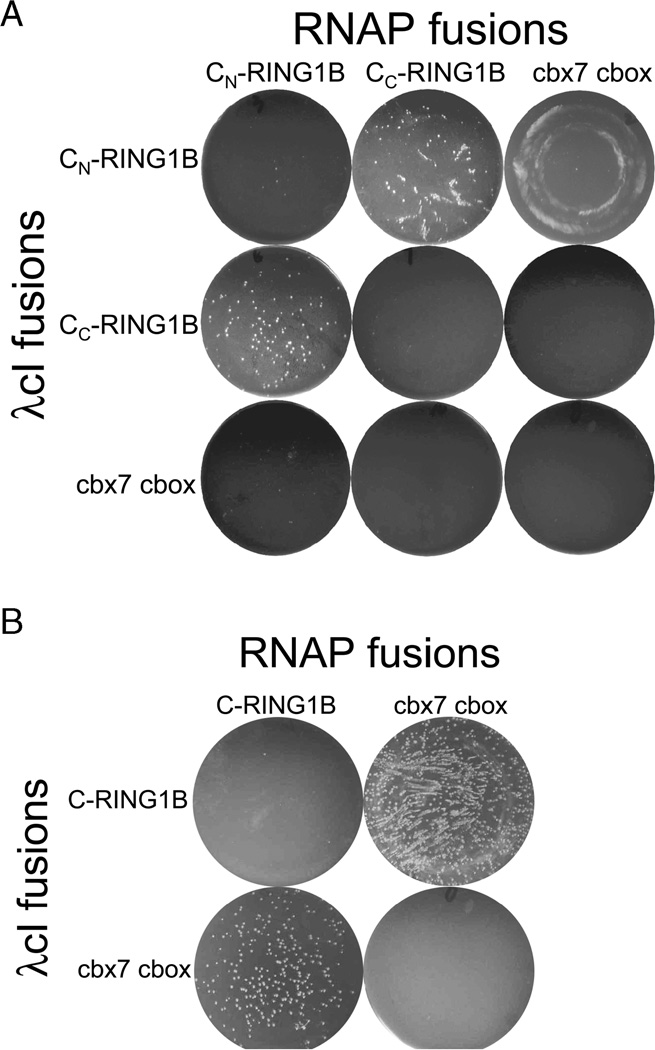
Figure 3.
C-RING1B is composed of two interacting subregions. (A) The bacterial two-hybrid assay utilizes the DNA binding properties of λ cI and the transcriptional activation properties of the N-terminal domain of RNA polymerase (RNAP). The two subregions of C-RING1B, CN-RING1B and CC-RING1B, are cloned as a fusion with either λ cI or RNAP and cotransformed into Bacteriomatch reporter cells (Strategene). Interaction between λ cI and RNAP fusion proteins results in the recruitment of RNAP to the promoter, activating transcription of the β-lactamase gene and conferring ampicillin resistance to the transformed bacteria. (B) Positive control showing the interaction between the entire C-RING1B and the cbx7 cbox domain.