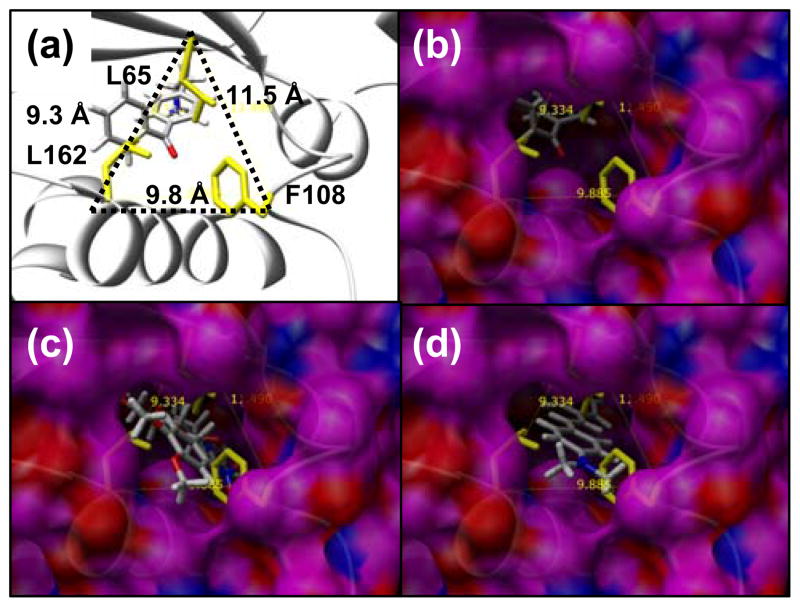
Figure 4.
Mutations L162A, F108A, and L65A open up the back of the binding site to be exposed to solvent - the “back door”. The position between these residues relative to helix (res:150–163), the crystallographic conformation of pBpa, and the β-sheet that covers the top of the binding site is shown in (A). The distance between the Cα atom of each of these three residues is shown in (A). A surface of the outside of the 8Ala synthetase is shown in (B, C, D) where the view through the solvent exposed back door shows ligands in the binding site. Residues L162, F108 and L65 are shown in yellow, but alanine residues at these positions contribute to the surface shown for the 8Ala synthetase. In (B) the crystallographic conformation of pBpa is shown, in (C) the lowest energy conformation of 7 in the 8Ala synthetase is shown, and in (D) the lowest energy conformation of the 2 is shown in the 8Ala synthetase. Successful designs for 7 and 2 required that the back door remained open and exposed to solvent. The best designs for 4 and 5 were successful in closing the back door so no part of the binding site is exposed to solvent in this region.