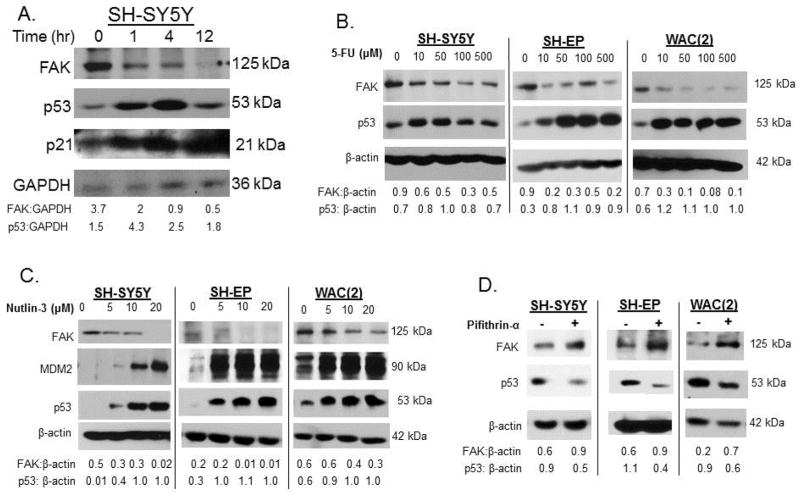
Figure 4.
Expression of FAK in neuroblastoma cell lines was inversely correlated to p53. A. SH-SY5Y cells were treated with 2Gy of irradiation to upregulate p53. Cells were harvested and lysates made at increasing times following irradiation. Immunoblotting was performed which showed an increase in p53 and p21 (indicating p53 activity) beginning at 1 hour post-irradiation. As p53 increased following irradiation, FAK protein decreased. B. Pharmacologic manipulation of p53 with 5-fluoruracil (5-FU) was examined. SH-SY5Y, SH-EP and WAC(2) cells were treated for 24 hours with increasing concentrations of 5-FU. Cell lysates were examined with immunoblotting. 5-FU treatment led to increased p53 and a decrease in FAK in all three cell lines. C. SH-SY5Y, SH-EP and WAC(2) cell lines were treated with increasing concentrations nutlin-3 for 48 hours and immunoblotting was performed on cell lysates. Increasing concentrations of nutlin-3 resulted in increased p53, and a concomitant decrease in FAK expression. D. Pifithrin-α was used to inhibit p53 in the SH-SY5Y, SH-EP and WAC(2) cells. Cell lines were treated with pifithrin-α (25 μM) for 48 hours and cell lysates examined for FAK and p53. In all three cell lines there was a decrease in p53 expression following pifithrin-α treatment, and an increase in FAK. Densitometry was performed on all of the blots and verified that p53 and FAK expression were inversely correlated.