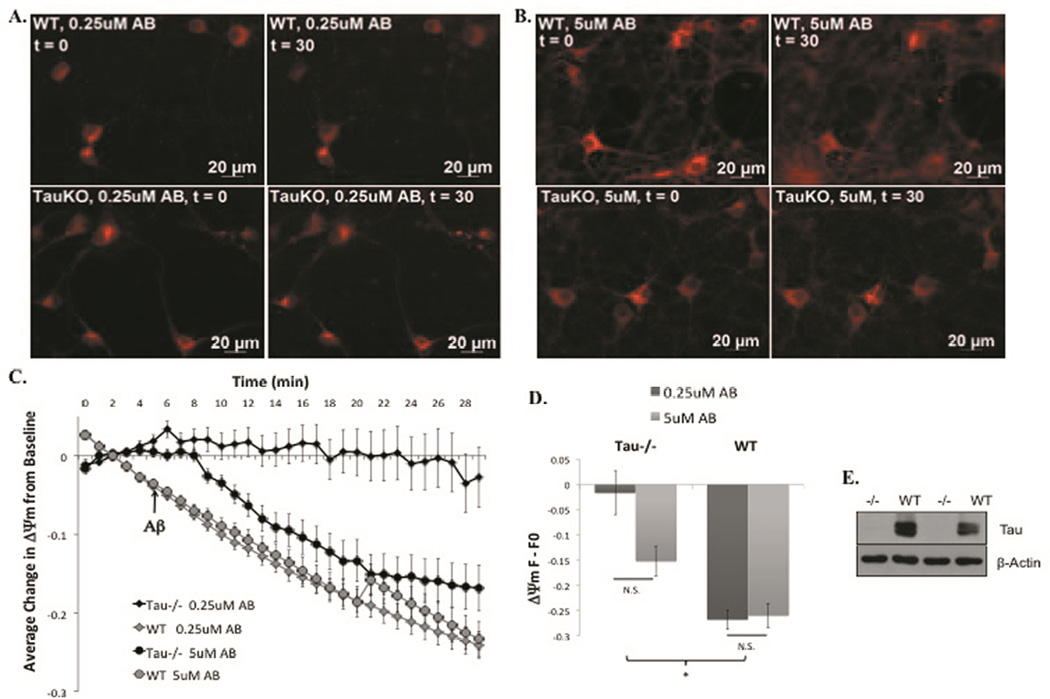
Figure 1. Tau−/− cortical neurons are protected from ΔΨm loss induced by low concentrations of Aβ42.
Representative images from t=0 (left) and t=30 (right) of WT (top) and tau−/− (bottom) primary cortical neurons loaded with ΔΨm indicator, MitoRed, and treated with 0.25µM (A) or 5µM Aβ42 (B). Quantification of full time-lapse experiments (C) and the change from t=0 to t=30 (D). Ablation of tau was confirmed via western blot analysis of cortical lysates from tau−/− and WT mouse brains using a tau polyclonal antibody and β-actin monoclonal antibody (E). *=P<0.05