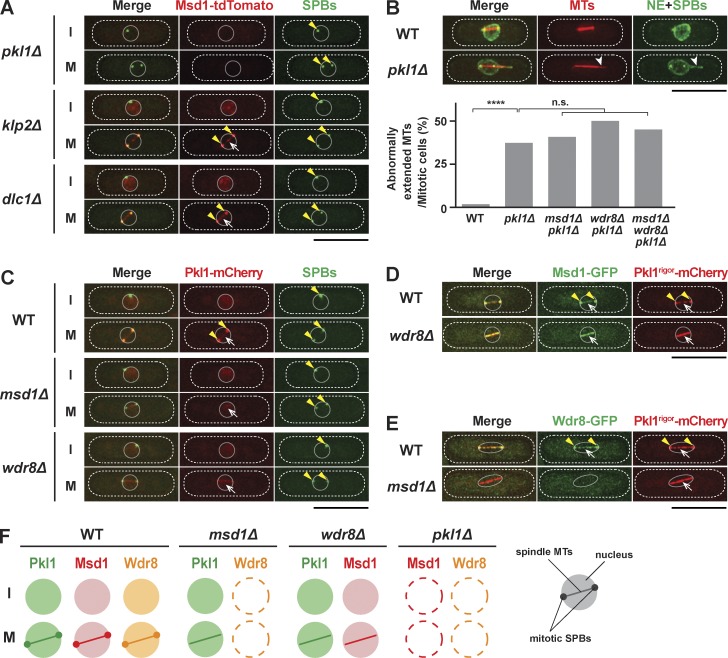
Figure 2.
Msd1 and Wdr8 act together with Pkl1/kinesin-14 for the anchorage of spindle microtubules to the SPB. (A) SPB localization of Msd1 requires Pkl1/kinesin-14. Localization of Msd1-tdTomato and GFP-Alp4 (SPBs) in pkl1Δ, klp2Δ, or dlc1Δ mutant cells during interphase (I) or mitosis (M) is shown. Cells were grown in rich media at 27°C. Note that Msd1 not only is localized to the mitotic SPB (arrowheads) and spindle microtubules (arrows) but is also recognizable in the interphase nucleus in klp2Δ and dlc1Δ, but not in pkl1Δ, cells. (B) pkl1Δ mutants display protruding spindle microtubules in the nucleus. Representative images of mitotic spindle microtubules with protrusion at one end in the pkl1Δ mutant cells containing mCherry-Atb2 (microtubules [MTs]), GFP-Alp4 (SPBs), and Cut11-GFP (nuclear envelope [NE]; West et al., 1998) are shown. A protruding spindle microtubule is indicated with arrowheads. The percentages of cells displaying protruding spindle microtubules in various mutants are shown at the bottom. All p-values are derived from the two-tailed χ2 test (≥40 cells; ****, P < 0.0001; n.s., not significant). (C) Msd1 and Wdr8 are required for Pkl1 localization to the SPBs but not to the spindle microtubules. Localization of Pkl1-mCherry and GFP-Alp4 (SPBs) in wild-type, msd1Δ, and wdr8Δ mutant cells during interphase (I) or mitosis (M) is shown. SPBs and spindle microtubules are indicated with arrowheads and arrows, respectively. (D) Msd1-GFP is colocalized with Pkl1rigor-mCherry on spindle microtubules in the wdr8Δ mutant. SPBs and microtubules are indicated with arrowheads and arrows, respectively. (E) Wdr8-GFP is delocalized in the Pkl1rigor mutant in the absence of Msd1. SPBs and spindle microtubules are indicated with arrowheads and arrows, respectively. (F) Summary of localization dependency between Msd1, Wdr8, and Pkl1. Schematic presentation of the mitotic nucleus, the SPB, and spindles is shown in the far right corner. The peripheries of the cell and the nucleus are outlined in the images (dotted and continuous lines, respectively). Bars, 10 µm.