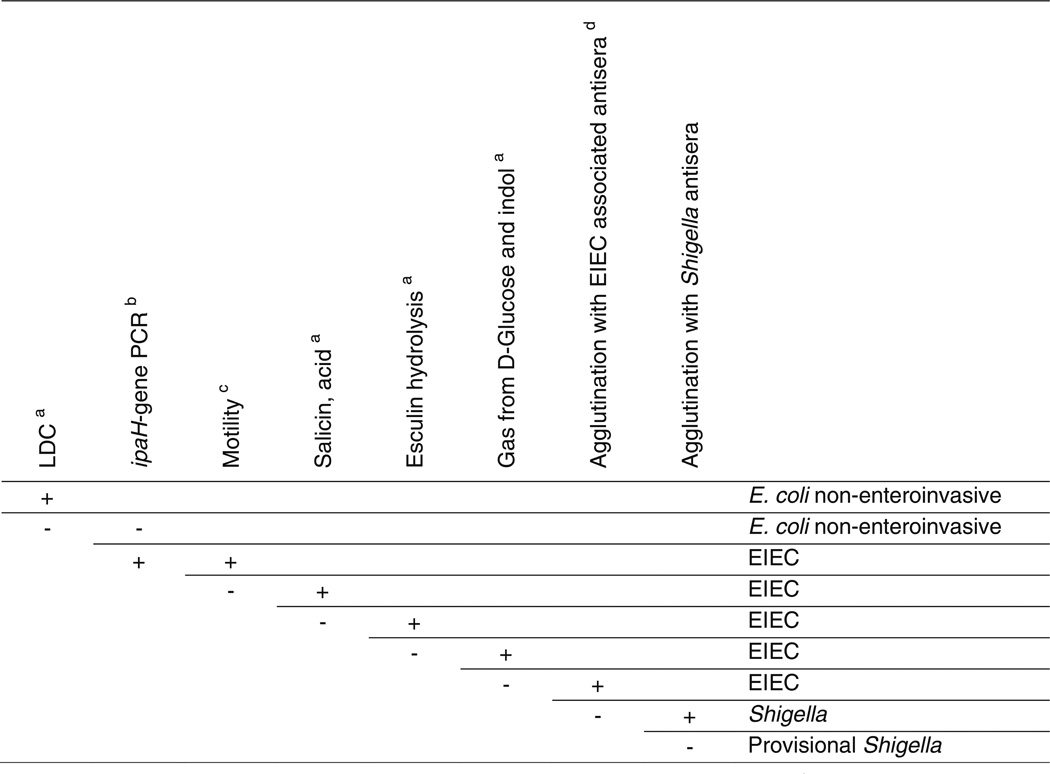
Figure 2.
Key for differentiation of Shigella, enteroinvasive Escherichia coli (EIEC), and noninvasive Escherichia coli. (From van den Beld MJ, Reubsaet FA. Differentiation between Shigella, enteroinvasive Escherichia coli (EIEC) and noninvasive Escherichia coli. European journal of clinical microbiology & infectious diseases : official publication of the European Society of Clinical Microbiology 2012;31(6):899–904; with permission)
- Based on Edwards and Ewing’s identification of Enterobacteriaceae, 4th edition, 1986 and/or Cowan and Steel’s manual for the identification of medical bacteria, 3rd edition, 1993.
- Performed with a standard PCR protocol, with primers designed to amplify a part of the conserved region of ipaH7.8, as described by Buysse et al., Microb. Pathog. 19(5):335–349.
- Incubated for 24 h in BHI-medium at 37°C.
- Known O:H serotypes of EIEC according to Bergey’s manual of Systematic Bacteriology, 2nd edition, volume 2, The Proteobacteria, Part B The Gammaproteobacteria.