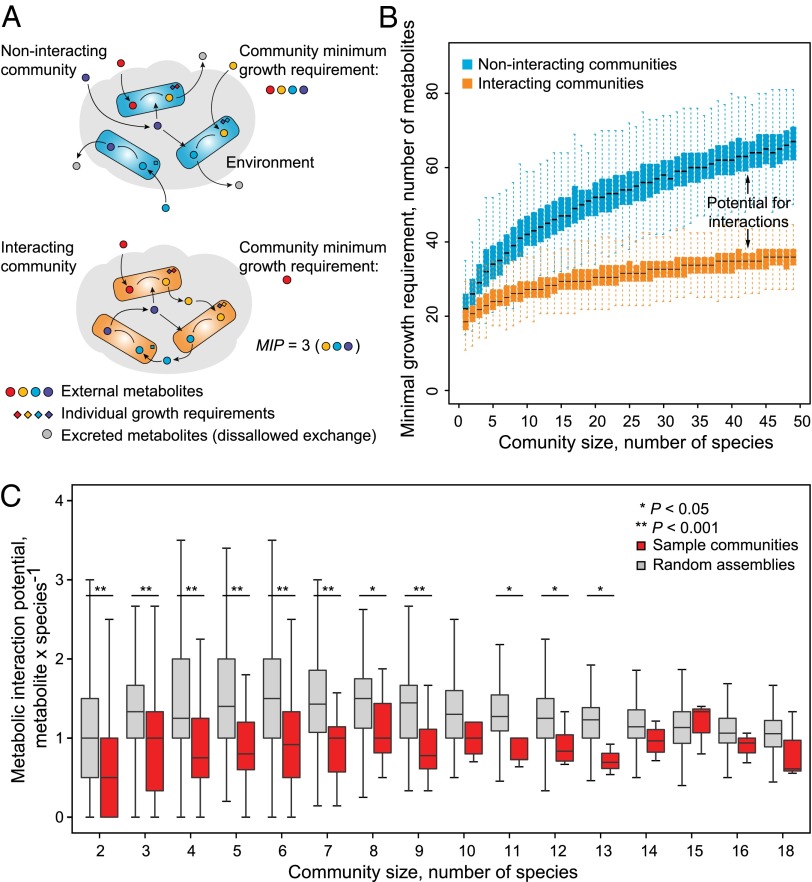
Fig. 3.
MIP of microbial communities. (A) Illustration of the concept of MIP. A community can use the biosynthetic capabilities of its members to decrease the collective dependence on nutritional availability from the environment. (B) MIP as a function of community size. For each community size, results of simulations based on 1,000 randomly assembled communities are shown. (C) Sample communities display lower than expected interaction potential in line with their high degree of resource competition.