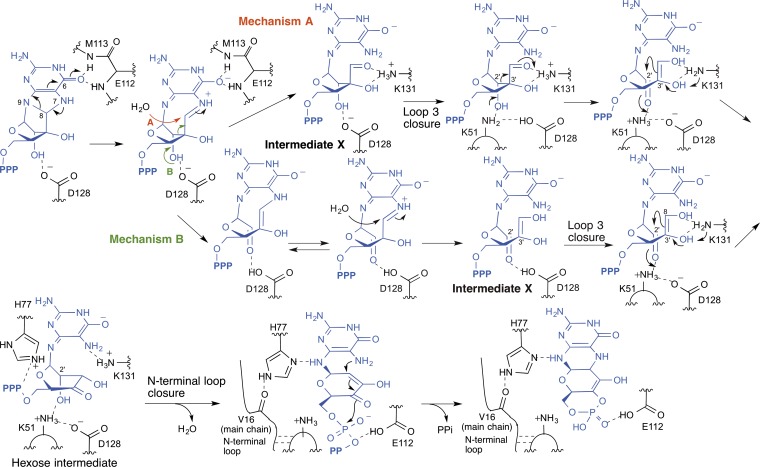
Fig. 5.
Proposed chemical mechanism of MoaC catalysis. MoaC initiates the reaction by stabilizing the anionic charge on O6, which results in either aminal hydrolysis (mechanism A), or C2′-C3′ bond cleavage (mechanism B). Shown are the structures of possible intermediates, including Intermediate X and the hexose intermediate, and the amino acid residues relevant to the chemistry of each step. See main text for details about the mechanism.