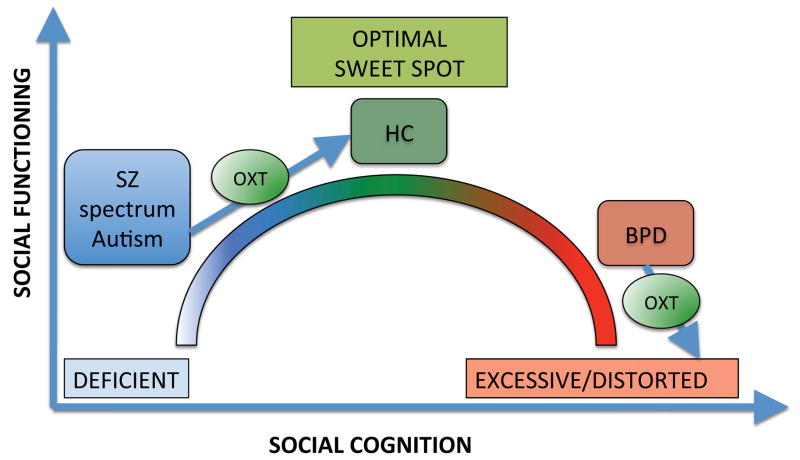
Figure 1. Interactionist Model of the Effect of Oxytocin on Social Cognition.
Oxytocin’s effects on social cognition and functioning are modulated by baseline social cognition skills. There is a sweet spot of oxytocinergic tone/social cognition (i.e., optimal emotion recognition, mentalizing, salience and attention to emotional stimuli) and social functioning, below which social cognition is deficient (as in schizophrenia and autism, with positive effects of exogenous oxytocin) and beyond which social cognition is excessive/distorted (as in borderline personality disorder, with potentially negative effects of exogenous oxytocin).