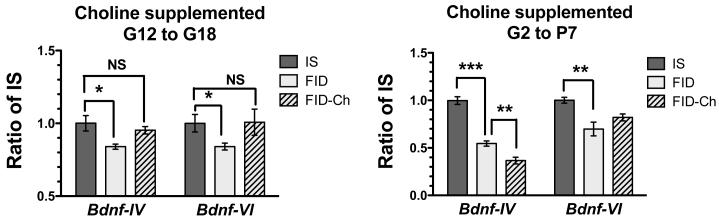
Figure 1.
The effect of targeted (left panel) versus universal (right panel) maternal choline supplementation during pregnancy and lactation on hippocampal BDNF gene expression in the iron sufficient adult offspring. Note that choline supplementation from gestational day 12 to 18 (FID-Ch) resulted in preserved BDNF levels in the offspring in adulthood compared to animals whose mothers were not treated with choline (FID). Levels of BDNF gene expression were similar to always iron sufficient (IS) animals. In contrast, non-targeted supplementation of the mother resulted in suppression of adult BDNF expression in the offspring.
* indicates a p-value<0.05.