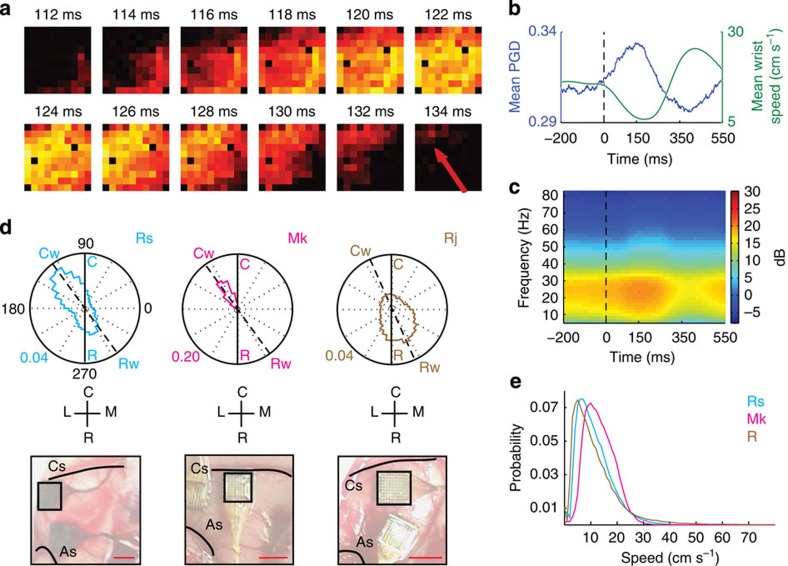
Figure 1. Properties of LFP beta waves.
(a) Temporal snapshots of the LFP voltages across the array indicating wave propagation. The LFP voltage on each electrode was band-pass filtered in the beta frequency range (that is, ±3 Hz centred at the beta peak of the power spectrum). Time in milliseconds labelled above each plot is with respect to the onset of the visual target. The red arrow in the bottom right panel shows the propagation direction of the wave. (b) Temporal evolution of the GOF measure of planar wave activity (PGD in blue ranging from 0.295 to 0.335, as well as the mean hand speed (green) ranging from 5 to 36 cm s−1. (c) Averaged spectrogram of a single-channel LFP revealing the temporal dynamics in beta frequency power relative to the visual target onset. (d) Circular distributions of wave propagation directions for monkeys Rs (cyan), Mk (magenta) and Rj (brown). A solid black line denotes the rostro–caudal axis on the cortical surface. A dashed line in each rose plot connecting Cw (caudal wave direction) and Rw (rostral wave direction) denotes the axis defined by the first or only mode of beta wave propagation axis. Each panel below the circular distributions depicts the location of the multielectrode arrays (4 × 4 mm) in the arm area of MI for the corresponding subject. A red horizontal bar in the right lower corner in each panel is 4 mm. Landmarks and orientations: Cs, central sulcus; As, arcuate sulcus; C, caudal; R, rostral; M, medial; L, lateral. (e) Distributions of estimated propagation speeds for monkeys Rs (cyan), Mk (magenta) and Rj (brown).