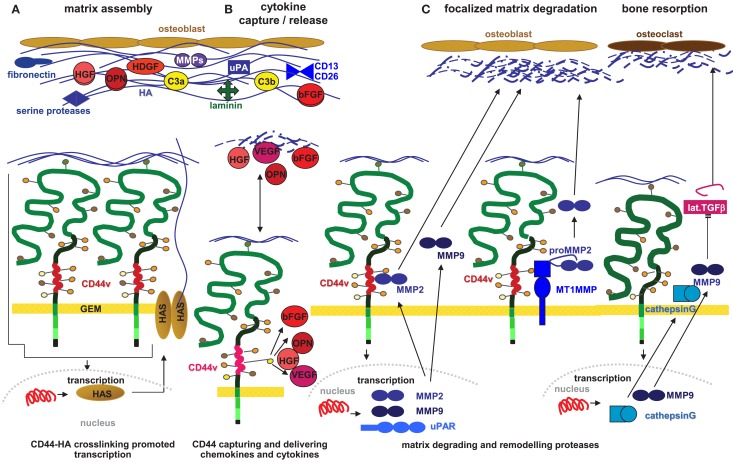
Figure 1.
The contribution of CD44 in HSC/LIC for assembly and modulation of the osteogenic niche. (A) HSC secrete large amounts of HA. Upon HA crosslinking, CD44 becomes activated, which supports transcription of HAS3, which strengthens the process of high MW HA deposition and incorporation of cytokines, chemokines, and proteases in the abundant HA coat. (B) HSC quiescence and LIC proliferation are supported by the catcher activity of CD44/CD44v6 and most pronounced CD44v3 associated GAG, which bind a large range of cytokines and chemokines including HGF, bFGF, OPN, and VEGF. (C) Particularly, LIC contribute to modulation of the matrix in the osteogenic niche. This is due to CD44-HA initiated transcription of MMP2, MMP9, uPAR, and cathepsinG. MMP2 and MMP9 bind to CD44; proMMP2 is cleaved by CD44v6-associated MT1MMP, which concomitantly allows for focal matrix degradation. CathepsinG and MMP9-activated TGFβ contributes to bone resorption and niche preparation for LIC.