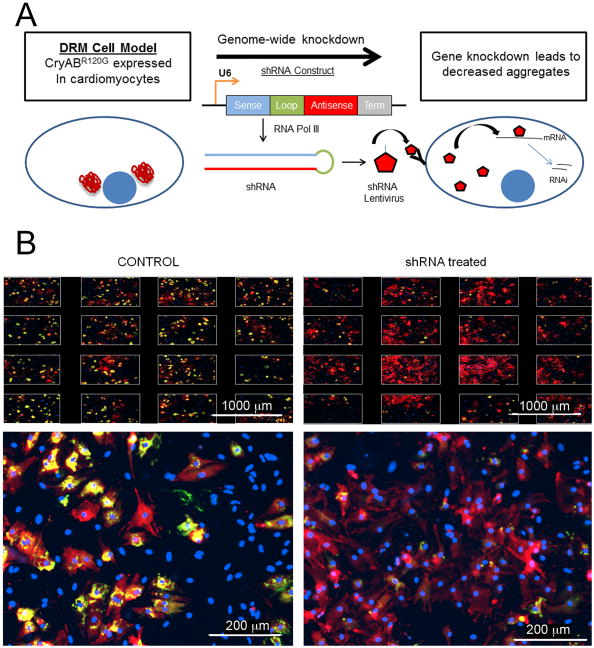
Figure 6.
High-throughput assay to uncover novel effectors of cardiac protein aggregation. A, Screening Principle. A cell model of cardiac proteotoxicity was developed in primary cardiomyocytes. These cells were subjected to systematic, genome-wide knockdown by infection with lentiviruses expressing shRNAs capable of being processed such that selective degradation of their cognate mRNAs took place. The goal of the screen is to find genes that, when knocked down, lead to a reduction of aggregates. B, An example of a candidate gene or “hit” in the screen. The top panels show the images taken from one well, in which 16 images are acquired and aggregate content quantified. The lower panel depicts one image from a well. In the well treated with siRNA, a drastic reduction in aggregate content is observed compared to controls. This figure demonstrates the very high signal to noise ratio observed upon expression of CryABR120G, which allows one to robustly quantitate changes in aggregate content. Scale bars: top panel, 1000 μm; bottom panel, 200 μm.