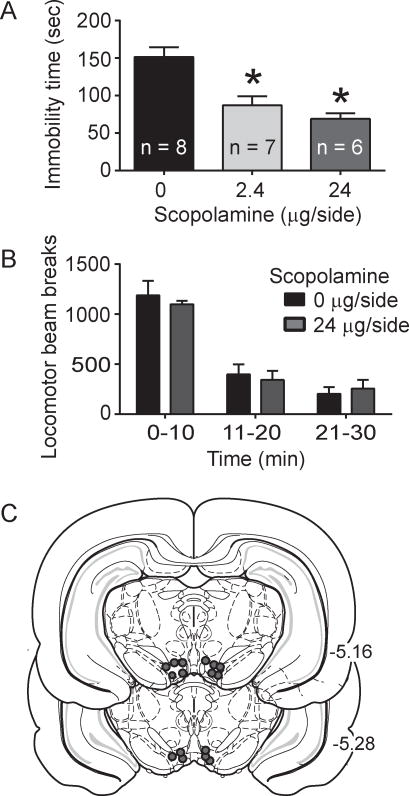
Fig. 3.
Intra-VTA scopolamine effects on the FST immobility time and total locomotor activity. A. Scopolamine infusion into the VTA led to decreased immobility in the FST (p < 0.001, main effect of drug; p < 0.05, Tukey post-hoc for 2.4 μg/side scopolamine versus saline; p < 0.05, Tukey post-hoc for 24 μg/side scopolamine versus saline). B. Intra-VTA infusion of 24 μg/side scopolamine did not alter locomotor activity, as measured by photobeam breaks (p > 0.05, two-way repeated measures ANOVA). C. Representative cannula placements for intra-VTA infusions in the scopolamine experiment.