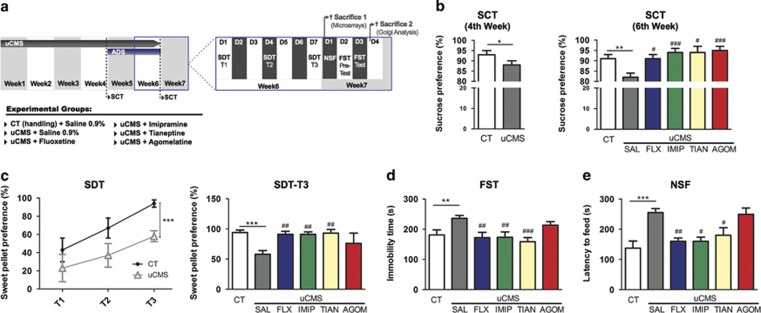
Figure 1.
Multi-dimensional behavioral characterization of the animal model of depression used (unpredictable chronic mild stress—uCMS) before and after treatment with four different ADs. (a) uCMS protocol was applied to the animals for 6 weeks; four different ADs (FLX, fluoxetine; IMIP, imipramine; TIAN, tianeptine; AGOM, agomelatine) were administered in the last 2 weeks of the uCMS protocol. Behavioral profiling was performed using a battery of tests to assess mood and anxiety-like behavior (n=8–12). Animals used for microarray analysis (n=3) were killed immediately after the end of uCMS protocol/AD-treatment (Sacrifice 1). Animals used for morphological analysis (n=5/6) were killed on week 7, after performing all behavioral tests (Sacrifice 2). (b) Sucrose consumption test (SCT) was performed at the fourth and sixth weeks of the uCMS protocol to evaluate anhedonia. uCMS induced an anhedonic profile in untreated rats (SAL), but all ADs reversed this phenotype. (c) Sweet Drive Test (SDT) was used as an additional measure of anhedonia. uCMS proved to induce anhedonia as observed in Trial 3 (T3; Trial 1 (T1) and Trial 2 (T2)—data not shown) that was reversed by FLX, IMIP, and TIAN but not AGOM. (d) In the Forced Swim Test (FST), uCMS induced increased immobility that was reversed by administration of FLX, IMIP, and TIAN but not AGOM. (e) uCMS exposure produced anxious-like behavior, as assessed in the Novelty Suppressed Feeding (NSF) test. All ADs, except AGOM reversed this phenotype. Error bars denote SEM. *Denotes the effect of uCMS-exposure; #Denotes the effect of ADs compared with untreated uCMS-exposed animals. */#p<0.05; **/##p<0.01; ***/###p<0.001. n=8–12 animals per group.