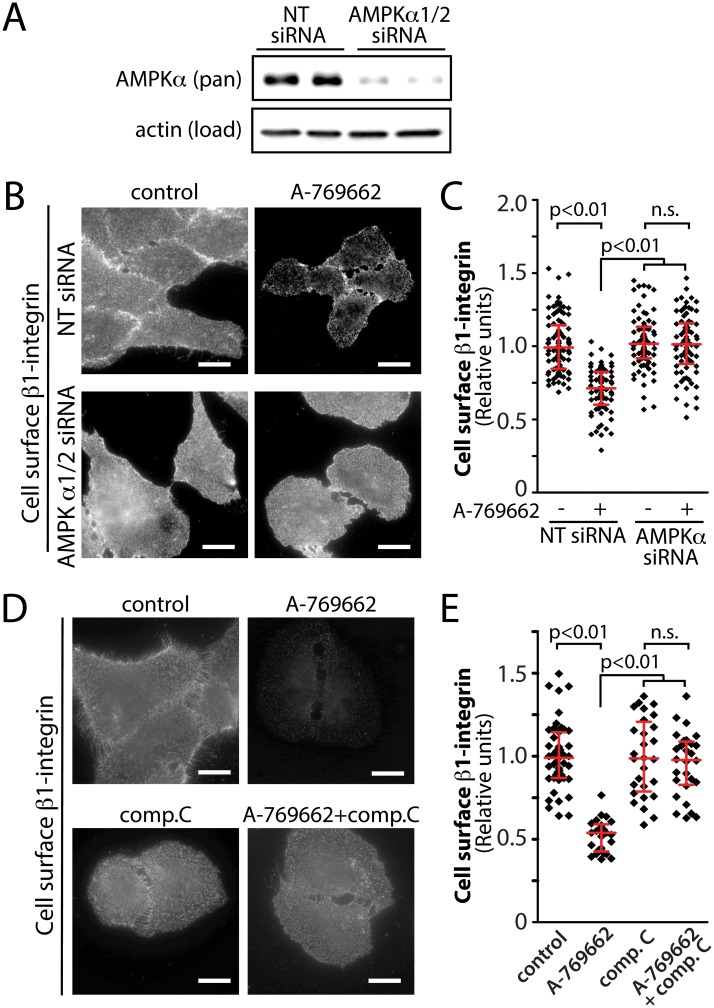
Fig 5. Inhibition of AMPK by siRNA gene silencing or by compound C prevents the reduction in cell surface β1-integrin elicited by A-769662 treatment.
(A-C) RPE cells were transfected with siRNA targeting AMPK α1/2 or non-targeting (NT, control) siRNA. (A) Whole cell lysates were prepared and resolved by immunoblotting and probed with anti-AMPK α1/2 or anti-actin antibodies. Shown are immunoblots representative of at least 3 independent experiments. (B) Following siRNA transfection, cells were treated with 100 μM A-769662 for 60 min as indicated. Intact cells were labeled with an antibody specific for an exofacial epitope on β1-integrin. Shown are representative fluorescence micrographs depicting cell surface β1-integrin fluorescence. Scale = 5 μm (C) Cell surface β1-integrin levels obtained by fluorescence microscopy were quantified. Shown are the cell surface β1-integrin measurements in individual cells (diamonds) as well as the median ± interquartile range of these values in each treatment condition (n = 3 independent experiments). (D) RPE cells were treated with 100 μM A-769662 or 40 μM compound C, alone or in combination, for 60 min as indicated. Intact cells were labeled with an antibody specific for an exofacial epitope on β1-integrin. Shown are representative fluorescence micrographs depicting cell surface β1-integrin fluorescence. Scale = 5 μm (E) Cell surface β1-integrin levels obtained by fluorescence microscopy as in (D) were quantified. Shown are the cell surface β1-integrin measurements in individual cells (diamonds) as well as the median ± interquartile range of these values in each treatment condition (n = 3 independent experiments).