Figure 1.
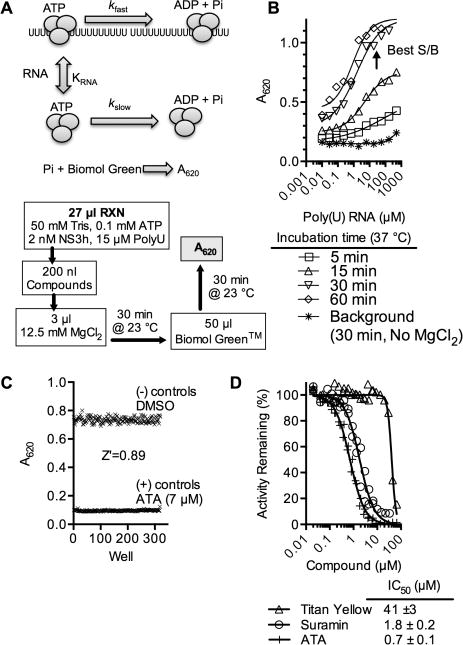
DENV helicase high-throughput ATPase assay. (A) Assay setup. DENV helicase (gray) cleaves ATP at a slow basal rate (kslow) and more rapidly in the presence of RNA (kfast). The Biomol Green reagent reacts with inorganic phosphate to produce a product that absorbs light at 620 nm. In automated screening, compounds are added to a reaction mix, and ATP hydrolysis is initiated with Mg2+. In addition to key reagents noted, all assays were performed at pH 7.5 and contained 5 μg/mL BSA, 0.01% (v/v) Tween 20, 5 mM DTT, and 0.3% DMSO (final concentration). (B) Effect of poly(U) RNA on inorganic phosphate released from ATP in the presence of 2 nM DENV NS3h after indicated times. Conditions with the best signal compared to control assays where reactions were not initiated with MgCl2 were chosen for HTS. (C) To assess assay quality, a Z′ factor33 was calculated by performing 192 positive control reactions (7 μM aurintricarboxylic acid (ATA)) and 192 negative control reactions (DMSO only) arranged in a checkerboard fashion in a 384-well plate. (D) Concentration–response assays using nonspecific helicase inhibitors.11, 34
