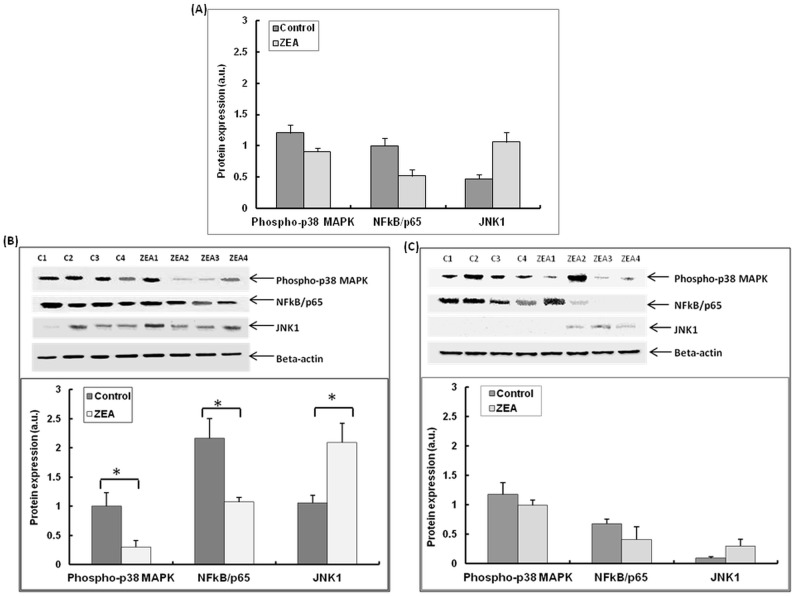
Fig 7.
A. Effect of ZEA diet on the phosphorylation level of MAPKs and NF-kB in total spleen lysates. Phospho-p38 MAPK, phspho-NF-kB/p65 and JNK1 expression level determined by using Western blot analysis, and expressed as ratio of phospho-p38 MAPK, phspho-NF-kB/p65 and JNK1 to β-actin band intensities. Results are expressed as arbitrary units (A.U.). Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA followed by Fisher test (* = P< 0.05, ZEA-contaminated spleen versus Control spleen).B. Effect of ZEA diet on the phosphorylation level of MAPKs and NF-kB in cytoplasmic spleen lysates. Phospho-p38 MAPK, phspho-NF-kB/p65 and JNK1 expression level determined by using Western blot analysis, and expressed as ratio of phospho-p38 MAPK, phspho-NF-kB/p65 and JNK1 to β-actin band intensities. Results are expressed as arbitrary units (A.U.). Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA followed by Fisher test (* = P< 0.05, ZEA-contaminated spleen versus Control spleen). C. Effect of ZEA diet on the phosphorylation level of MAPKs and NF-kB in nuclear spleen lysates. Phospho-p38 MAPK, phspho-NF-kB/p65 and JNK1 expression level determined by using Western blot analysis, and expressed as ratio of phospho-p38 MAPK, phospho-NF-kB/p65 and JNK1 to β-actin band intensities. Results are expressed as arbitrary units (A.U.). Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA followed by Fisher test (* = P< 0.05, ZEA-contaminated spleen versus Control spleen).