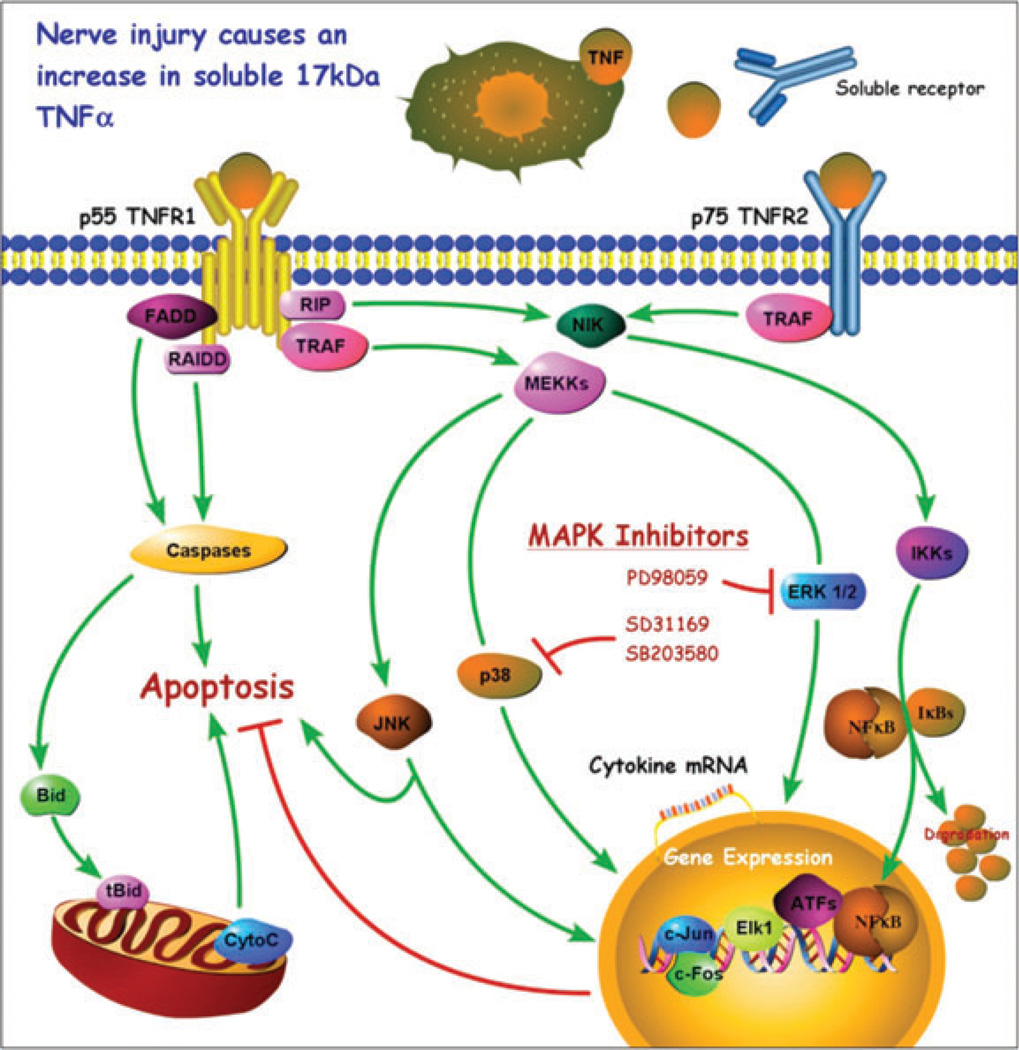
Figure 1.
A model diagram of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) signaling. TNF-α is enzymatically cleaved from a 26-kDa cell-surface-bound monomer by TNF-α-converting enzyme to form a 17-kDa soluble cytokine that is a target for therapeutic sequestration by soluble receptors. Both forms of TNF-α can interact with either of two distinct receptors, p55TNFR1 and p75TNFR2. Receptor-mediated effects can trigger cell activation, cytokine suppression, cytokine upregulation, or apoptosis, depending on the complex interactions between the pathways illustrated. Interactions between the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway and the JNK pathway are especially important. p38 inhibitors are of particular interest because of their relationship to gene expression which can result in reduction of TNF-α protein expression.