Figure 1. Core metabolic principles.
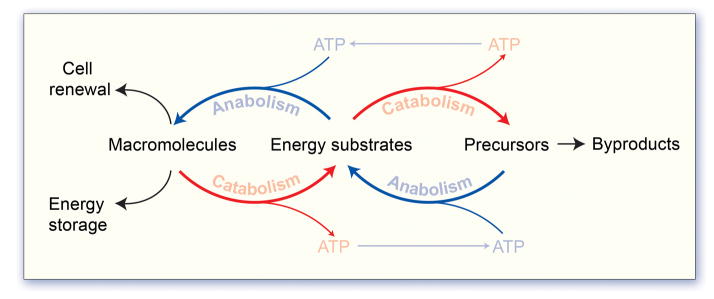
Vital processes are fueled though the metabolism of energy substrates supplied by the environment, such as glucose, fatty acids and amino acids. Catabolism, the process of breaking down (oxidizing) metabolites to produce energy, and anabolism, the process of constructing macromolecules from precursors, are intimately balanced such that catabolic products, including hydrocarbons and energy in the form of ATP and reducing cofactors (NADPH), serve as substrates for the anabolic production of macromolecules that cannot be obtained from the environment. Macromolecules that include lipids, proteins, nucleotides and glycogen represent a cellular energy reserve, and also compose the essential building blocks for cell renewal.
