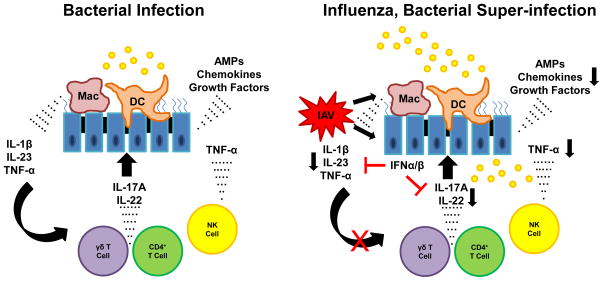
Figure 3.
Influenza infection results in inhibition of Type 17 immunity in the lung. Bacterial infection induces robust IL-17, IL-22, and TNF-α production in the lung. This process mediates inflammation and antimicrobial host defense. In the context of preceding influenza (IAV), type I IFNs inhibit Type 17 immunity by attenuating IL-1β and IL-23 production by macrophages and dendritic cells. IL-17A and IL-22 production by γδ and CD4+ T cells is markedly reduced resulting in impaired host defense against bacterial challenge.