Figure 8.
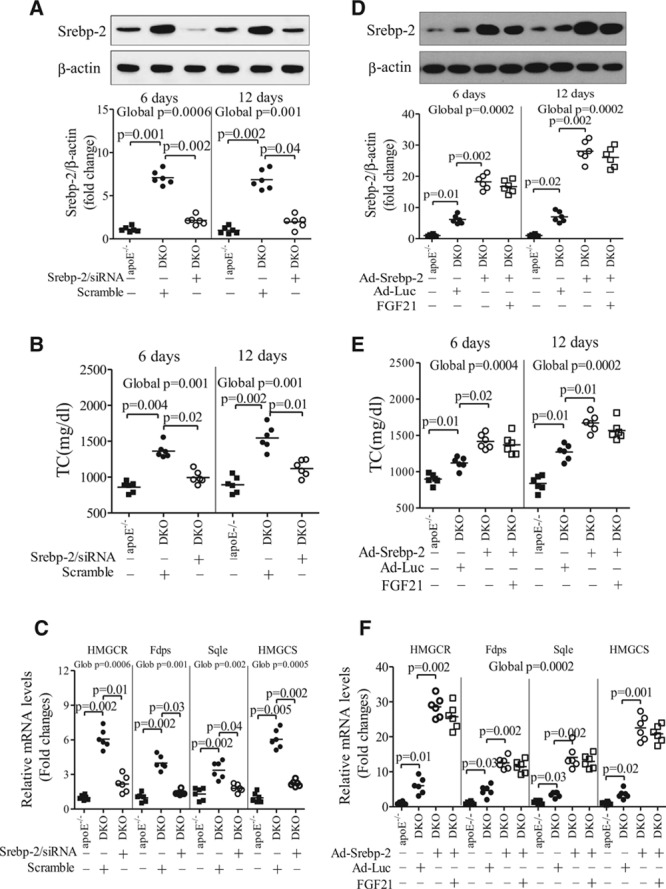
Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) 21 decreases hypercholesterolemia via inhibition of hepatic sterol regulatory element-binding protein (Srebp)-2. A–C, Apolipoprotein (apo) E−/−FGF21−/− (DKO) mice were infected with adenovirus encoding small interfering RNA (siRNA) specific to Srebp-2 or scrambled control (5×108 plaque-forming units per mouse) for various periods. Age-matched apoE−/− mice were used as a control. A, Protein expression levels of hepatic Srebp-2 at day 6 and day 12 after adenoviral infection. B, Circulating levels of total cholesterol (TC) and (C) the expression levels of cholesterologenic genes determined by real-time polymerase chain reaction analysis at day 12 (n=6). D and E, DKO mice were infected with adenovirus encoding Srebp-2 (Ad-Srebp-2) or luciferase (Ad-Luc) for 6 days (as control), followed by treatment with daily intraperitoneal injection of recombinant mouse (rm) FGF21 (0.1 mg/kg per day) for another 6 days. D, The protein expression levels of Srebp-2 in the liver and (E) serum levels of total cholesterol. F, The mRNA expression of cholesterologenic genes at 12 days after adenoviral infection (n=6). Data are presented as dot plots with the line indicating the median. The global significance among 3 groups was determined by Kruskal-Wallis test, followed by pairwise comparisons with the Dunn-Sidak procedure.
