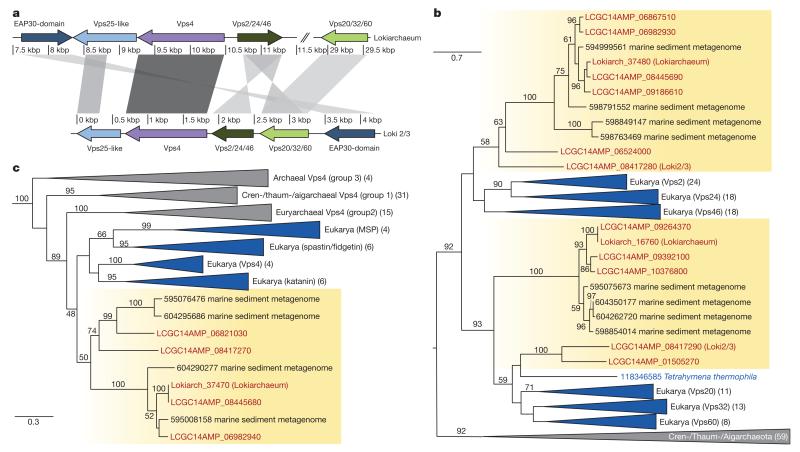
Figure 4. Identification of ESCRT components in the Lokiarchaeum genome.
a, Schematic overview of ESCRT gene clusters identified in Lokiarchaeum and Loki2/3. Intensity of shading between homologous sequences is correlated with BLAST bit score. b, Maximum-likelihood phylogeny of 207 aligned amino acid residues of ESCRT-III homologues identified in Lokiarchaeum, LCGC14AMP and other archaeal lineages. Eukaryotic homologues include the two distantly related families Vps2/24/46 and Vps20/32/60. Bootstrap support values above 50 are shown. c, Maximum-likelihood phylogeny of 388 aligned amino acid residues of AAA-type Vps4 ATPases including representatives for each of the four major eukaryotic sub-groups (membrane scaffold protein (MSP), katanin, spastin/fidgetin and Vps4) as well as homologues identified in the Lokiarchaeum genome, in LCGC14AMP and in sequenced archaeal genomes. Bootstrap support values below 45 are not shown. b, c, Scale indicates the number of substitutions per site. Numbers in brackets refer to the number of sequences in the respective clades.