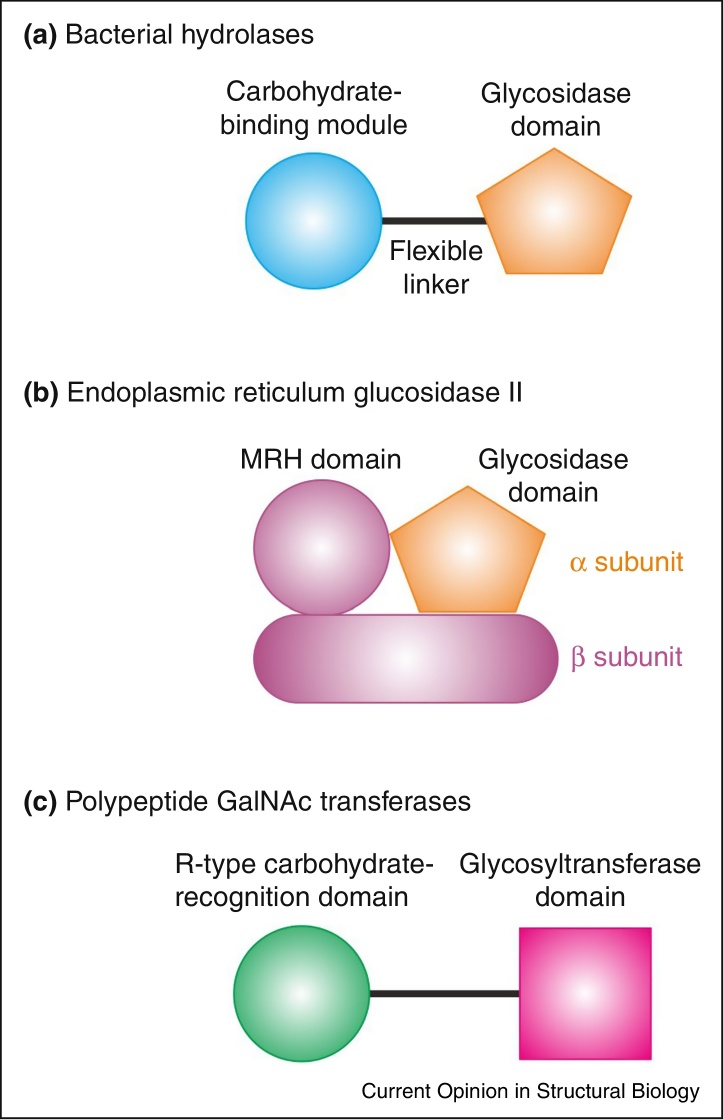
Figure 3.
Association of carbohydrate-recognition domains with enzymatically active domains. (a) One or more carbohydrate-binding modules are often linked to bacterial glycosidases and cellulose-degrading enzymes in a single polypeptide. The carbohydrate-binding modules localize the activity on substrates and enhance the activity of enzymes. (b) The α subunit of endoplasmic reticulum glucosidase II contains the glucosidase active site, but the activity of the enzyme on high mannose oligosaccharides that bear terminal glucose residues on one branch is enhanced by the β subunit, which contains an MRH domain that binds mannose on another branch of the oligosaccharide. (c) R-type carbohydrate-recognition domains in many of the polypeptide GalNAc transferase proteins direct the enzyme to regions of substrate glycoproteins that already bear one or more GalNAc residues.