Abstract
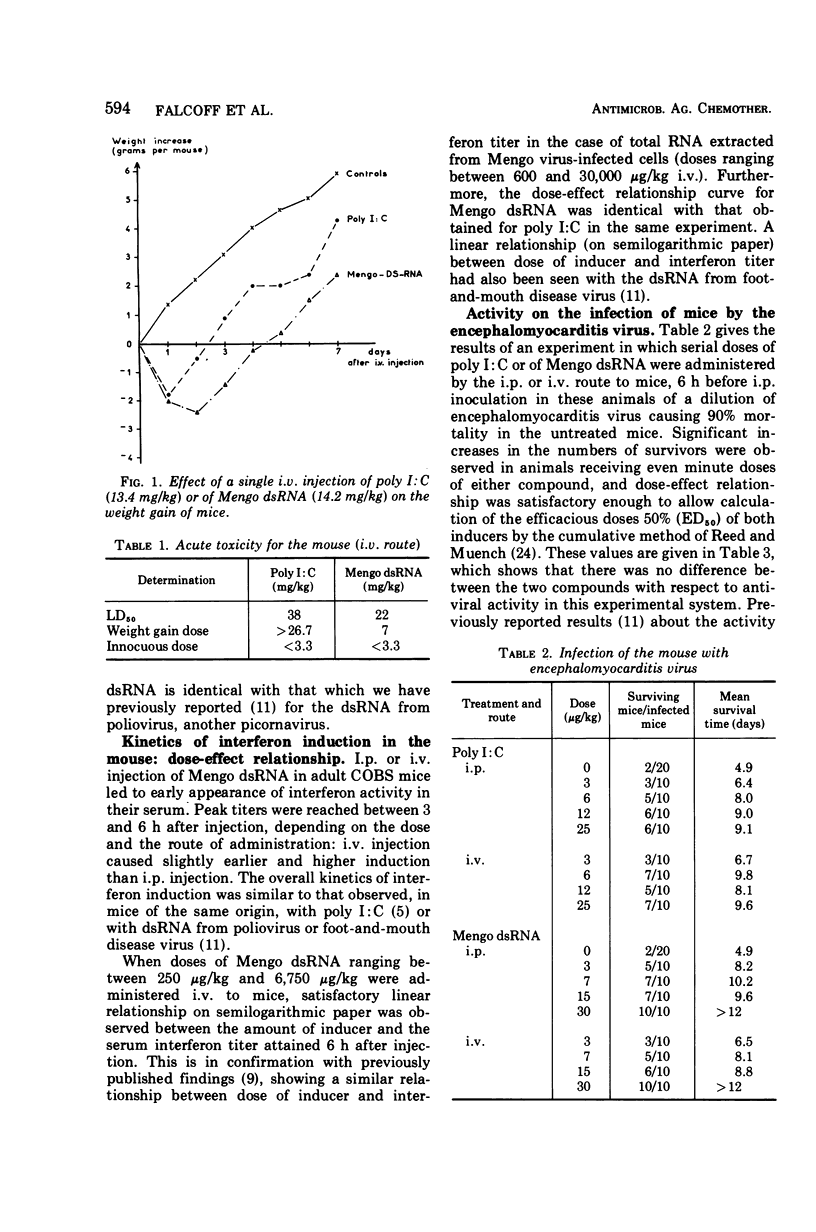
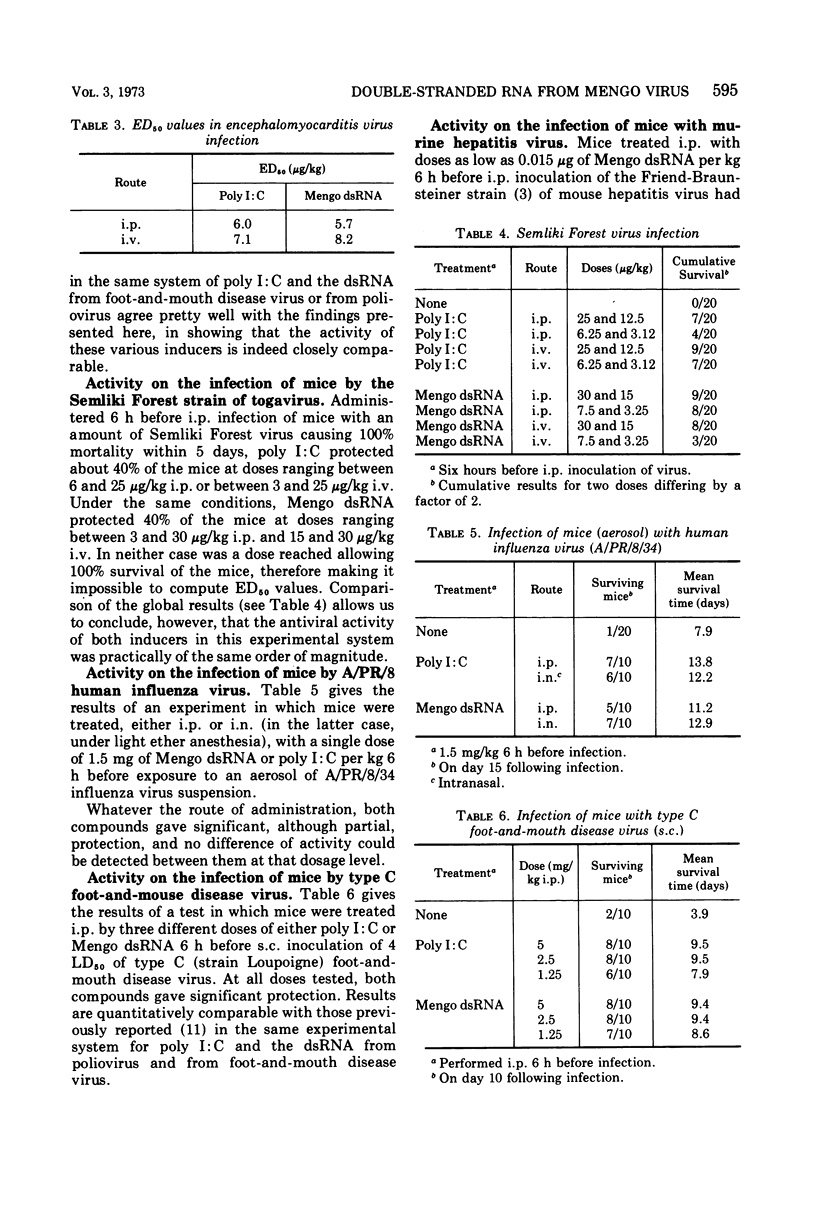
Mengo virus double-stranded ribonucleic acid (dsRNA) was obtained on a semi-industrial scale from infected cultures of BHK-21 cells grown in suspension. Yield of the extraction and purification operations was small (about 22 mg from 1011 cells in a 100-liter culture). Physicochemical characterization of this dsRNA gave an estimated molecular weight close to 4 × 106, a density of 1.59 (similar to that of the poliovirus dsRNA), and a thermal transition midpoint of 94 C. This product was a little more toxic for the mouse, by the intravenous route, than polyriboinosinic · polyribocytidylic acid (poly I:C) and strictly comparable in this respect to poliovirus dsRNA. The interferon-inducing capacity in the mouse and the antiviral activities in the mouse (infected with encephalomyocarditis, Semliki Forest, influenza, foot-and-mouth disease, and murine hepatitis viruses) and in the rabbit (Shope fibroma virus) of the ultraviolet light-inactivated product were practically identical, on a quantitative basis, with those of poly I:C. In vitro and in vivo experiments showed the dsRNA from Mengo virus to be slightly but significantly more resistant than poly I:C to the inactivating effect of human serum.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRAUNSTEINER H., FRIEND C. Viral hepatitis associated with transplantable mouse leukemia. I. Acute hepatic manifestations following treatment with urethane or methylformamide. J Exp Med. 1954 Dec 1;100(6):665–674. doi: 10.1084/jem.100.6.665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRUYET P., MEIGNIEN-GAUTHIER C., DELAUNAY A. A propos du dosage des transaminases sériques; mise au point d'une technique personnelle. Ann Biol Clin (Paris) 1958 Oct-Dec;16(10-12):661–669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banks G. T., Buck K. W., Chain E. B., Darbyshire J. E., Himmelweit F. Penicillium cyaneo-fulvum virus and interferon stimulation. Nature. 1969 Jul 12;223(5202):155–158. doi: 10.1038/223155a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. M., Koch G. Infectious replicative intermediate of poliovirus: purification and characterization. Virology. 1969 Apr;37(4):521–534. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90270-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CDe Clercq E., Eckstein F., Sternbach H., Merigan T. C. The antiviral activity of thiophosphate-substituted polyribonucleotides in vitro and in vivo. Virology. 1970 Oct;42(2):421–428. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90285-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherby J., Werner G. H. Activité du complexe bicatenaire acide polyriboinosinique acide polyribocytidylique (poly I:C) sur l'infection de la souris par divers virus. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1970 Dec;119(6):756–760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIEND C., WROBLEWSKI F., LA DUE J. S. Glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase activity of serum in mice with viral hepatitis. J Exp Med. 1955 Dec 1;102(6):699–704. doi: 10.1084/jem.102.6.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falcoff R., Falcoff E. T. Induction de la synthèse d'interféron par des RNA bicaténaires. I. Application à l'étude du cycle de multiplication du virus Mengo. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Jun 17;182(2):501–510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falcoff R., Falcoff E., Catinot L. Interferon induction by and infectivity of ultraviolet-irradiated double- and multistranded viral RNA's. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Sep 17;217(1):195–198. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(70)90137-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falcoff R., Falcoff E. Mise en évidence des acides ribonucléiques bicaténaires pendant le cycle de multiplication virale par l'induction d'interféron chez la souris. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1969 Mar 17;268(11):1559–1562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fayet M. T., Branche R., Falcoff E., Falcoff R., Cherby J., de Ratuld Y., Werner G. H. Study of two double-stranded ribonucleic acids of viral origin: interferon inducing and antiviral activities. Prog Immunobiol Stand. 1971;5:267–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field A. K., Lampson G. P., Tytell A. A., Nemes M. M., Hilleman M. R. Inducers of interferon and host resistance, IV. Double-stranded replicative form RNA (MS2-Ff-RNA) from E. coli infected with MS2 coliphage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Nov;58(5):2102–2108. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.5.2102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field A. K., Tytell A. A., Lampson G. P., Hilleman M. R. Inducers of interferon and host resistance. II. Multistranded synthetic polynucleotide complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Sep;58(3):1004–1010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.3.1004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field A. K., Young C. W., Krakoff I. H., Tytell A. A., Lampson G. P., Nemes M. M., Hilleman M. R. Induction of interferon in human subjects by poly I:C. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Apr;136(4):1180–1186. doi: 10.3181/00379727-136-35454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fournel J., Ganter P., Koenig F., de Ratuld Y., Werner G. H. Antiviral activity of distamycin A. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1965;5:599–604. doi: 10.1128/AAC.5.6.599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin R. M. Purification and properties of the replicative intermediate of the RNA bacteriophage R17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jun;55(6):1504–1511. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.6.1504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin R. M. Replication of bacteriophage ribonucleic acid: some physical properties of single-stranded, double-stranded, and branched viral ribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1967 Feb;1(1):64–75. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.1.64-75.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEARST J. E., VINOGRAD J. The net hydration of T-4 bacteriophage deoxyribonuecleic acid and the effect of hydration on buoyant behavior in a density gradient at equilibrium in the ultracentrifuge. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1961 Jul 15;47:1005–1014. doi: 10.1073/pnas.47.7.1005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LATARJET R., MORENNE P., BERGER R. Un appareil simple pour le dosage des rayonnements ultraviolets émis par les lampes germicides. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1953 Aug;85(2):175–184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampson G. P., Tytell A. A., Field A. K., Nemes M. M., Hilleman M. R. Inducers of interferon and host resistance. I. Double-stranded RNA from extracts of Penicillium funiculosum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Aug;58(2):782–789. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.2.782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordlund J. J., Wolff S. M., Levy H. B. Inhibition of biologic activity of poly I: poly C by human plasma. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Feb;133(2):439–444. doi: 10.3181/00379727-133-34492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern R. A nuclease from animal serum which hydrolyzes double-stranded RNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Nov 9;41(3):608–614. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90056-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tytell A. A., Lampson G. P., Field A. K., Hilleman M. R. Inducers of interferon and host resistance. 3. Double-stranded RNA from reovirus type 3 virions (reo 3-RNA). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Oct;58(4):1719–1722. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.4.1719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VERGE J., PARAF A., DHENNIN L., ASSO J. Adaptation du virus aphteux au lapin nouveau-né. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1957 Jun 17;244(25):3098–3100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


