Figure 4.
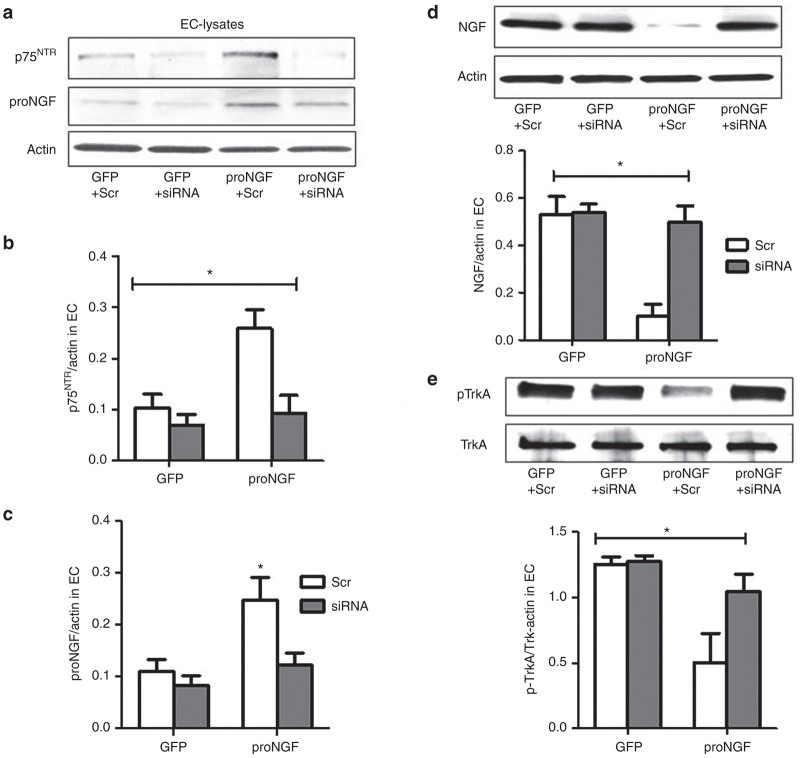
Expression of proNGF is dependent on p75NTR in EC. Human retinal ECs were transduced with one of the followings: pGFP plus scrambled siRNA (GFP+Scr), pGFP plus siRNA against p75NTR (GFP+siRNA); pGFP-proNGF123, a mutant cleavage resistant form of proNGF, plus scrambled siRNA (proNGF+Scr); pGFP-proNGF123 plus siRNA against p75NTR (proNGF+siRNA), and cell lysate and supernatant were collected after 48 hours. (a,b) Representative western blots statistical analysis of total p75NTR expression normalized to actin. (a,c) Representative western blots and statistical analysis of proNGF expression normalized to actin. 2 × 2 analysis showed interaction between proNGF overexpression and silencing p75NTR. Silencing p75NTR significantly reduced its expression in both GFP-controls and proNGF-groups. Results showed that overexpression of proNGF induced p75NTR expression and that silencing p75NTR downregulated proNGF expression in EC. Results presented as mean ± SD. n = 5–6 per group. *P < 0.05 versus other groups. (d) Representative western blots and statistical analysis of NGF expression normalized to actin in EC. (e) Representative western blots and statistical analysis of TrkA activation normalized to total TrkA. 2 × 2 analysis demonstrated interaction between proNGF overexpression and silencing p75NTR. Overexpression of proNGF resulted in significant decreases in NGF levels and activation of its TrkA receptor compared with GFP-controls. Silencing p75NTR expression increased NGF levels and enhanced TrkA activation in proNGF overexpressing cells. Results are expressed as mean ± SD. n = 5 per group. *P < 0.05 versus other groups.