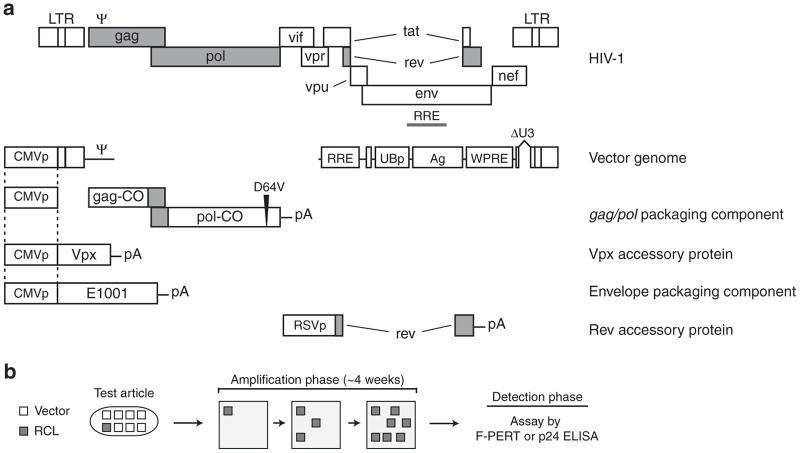
Figure 1.
Schematic of the VP02 vector system and a generic replication-competent lentivirus (RCL) assay. (a) Structure of wild-type HIV-1 and the five components of the VP02 vector system. Regions of homology between vector components are marked by dotted lines. The vector genome encodes a modified ubiquitin promoter (UBp) upstream of an antigen (Ag), the woodchuck hepatitis post-transcriptional regulatory element (WPRE), and an extended deletion within the U3 and 3′-PPT regions (ΔU3). The gag/pol vector component has been codon-optimized to reduce homology to wild-type HIV-1; however, the sequence of the frame-shift region has been maintained to ensure proper translation of the Gag and Gag-Pol polypeptides. In addition, the pol gene encodes a D64V point mutation within the catalytic site of the Integrase protein to abrogate Integrase-dependent vector integration. VP02 contains two accessory proteins: Vpx from SIVmac and Rev from HIV-1. Shaded regions denote HIV-1 sequence conserved in the VP02 vector system. VP02 is pseudotyped with the heterologous envelope glycoprotein E1001. (b) Diagram of standard cell culture-based RCL assays. Vector product (test article) is used to transduce permissive amplification cells. Small amounts of replication-competent virus which may be present in the original test article are expected to replicate during subsequent cell passages (amplification phase). Following ~4 weeks in cell culture, cell supernatant is analyzed for the presence of virus using a sensitive detection method for components of the virus particle (p24 by ELISA) or RT enzymatic activity (F-PERT assay). F-PERT, fluorescent-product enhanced reverse transcriptase; SIV, simian immunodeficiency virus.