Figure 4.
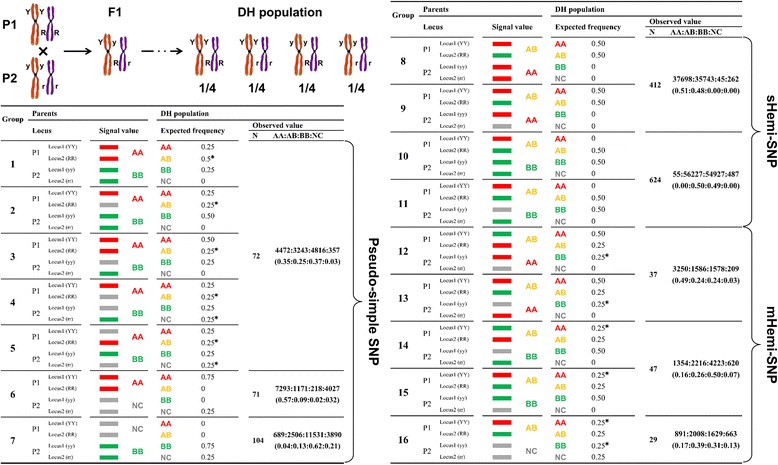
Possible genotypes derived from inter-homoeologues targeted by a given SNP probe and their frequency in the HJ-DH population. Considering the two inter-homoeologous sequences YY and RR in P1 and their alleles yy and rr in P2 as two independent loci in the genome, the DH population will expect four genotypes of YYRR, YYrr, yyRR, and yyrr with a frequency of 1/4 for each (top left). Fluorescence signals of the parental lines are assigned as AA (C/G base, red), BB (A/T base, green) and AB (heterozygosis, orange), respectively. In the case of a null locus, the miss signal is assigned as NC (grey). In Pseudo-simple SNP type (lower left), only a same set of signals as Simple SNP are detected in the parental lines but there will be non-parental genotypes (NPGs) segregation in the DH population in Group 1-5. In sHemi-SNP type, there will be AB (heterozygous) signal detected due to presence of hemi-SNP but there will no NPG in the DH population (top right). In mHemi-SNP type, the signal values are similar to sHemi-SNP in parental lines but there will be NPG signals detected in the DH populations due to multiple mismatched nucleotides within the inter-homoeologous sequences (lower right). The color bars can be used for calculation of signal values in the DH population (expected frequency). “*” marks the NPGs occurred in the DH population. N is the number of the polymorphic SNPs in indicated group(s). The numbers of each signal for corresponding SNP group in the 179 DH lines are listed in the column of AA:AB:BB:NC. The number in the bracket refers to the ratio for each signal (genotype).
