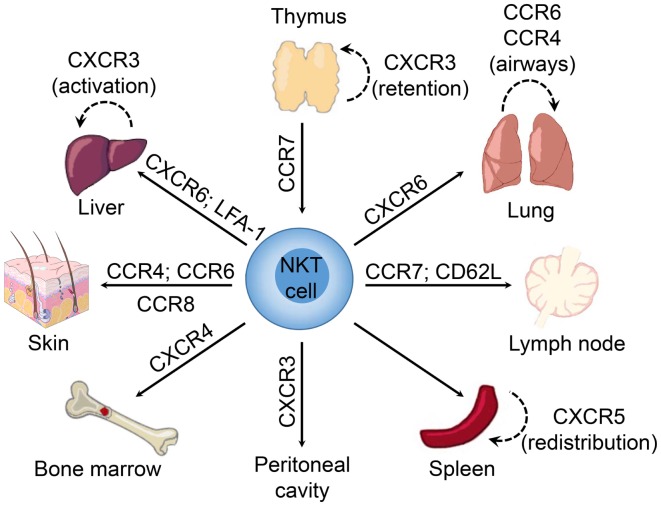
Figure 1.
Chemokine receptors involved in tissue-dependent NKT cell homing. Following their development in the thymus, NKT cells emigrate to peripheral tissues (including liver, spleen, lung, bone marrow, lymph nodes, skin, and the peritoneum) where their accumulation and/or retention is regulated by adhesion molecules and chemokine–chemokine receptor interactions. Chemokine receptors and adhesion molecules associated with NKT cell redistribution within these tissues are indicated.