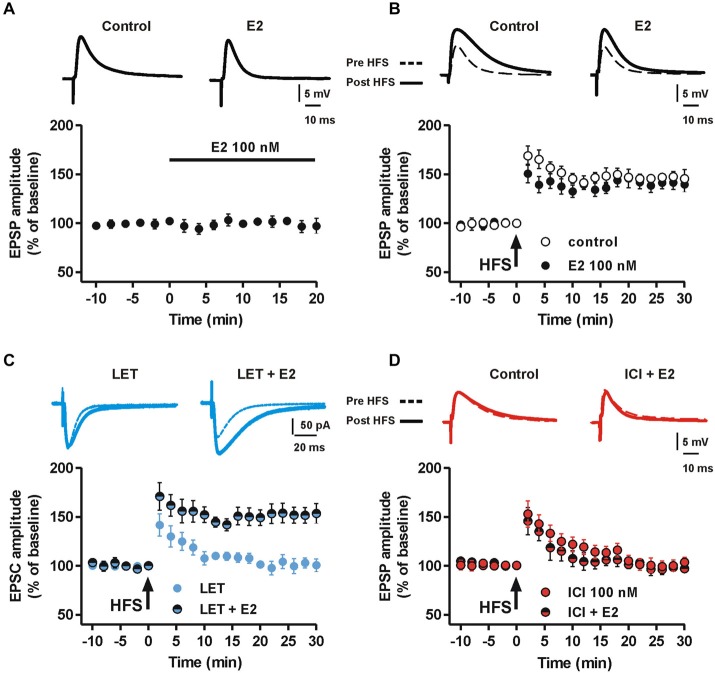
Figure 3.
Effect of E2 on synaptic transmission and the LTP in the presence of aromatase inhibition and ER blockade. (A) Time-course of the EPSP amplitudes recorded from a group of MSNs before and after the application of 100 nM E2 for 20 min. Upper traces show EPSPs recorded from a MSN in control condition and 20 min after E2 application. (B) Time-course graph showing the LTP induced by HFS protocol in control conditions and in the presence of 100 nM E2. Upper pairs of traces showing EPSPs measured before and 30 min after the delivery of HFS protocol to induce LTP. (C) Time-course of the EPSC amplitude acquired before and after the application of the HFS protocol from a group of MSNs in the presence of 100 nM LET or LET plus 100 nM E2. Upper superimposed traces showing the EPSC traces acquired from MSNs before and 30 min after the HFS protocol. Note that E2 is able to induce LTP in the presence of ARO inhibition. (D) Time-course of the EPSP amplitude of MSNs recorded in the presence of 100 nM ICI or ICI plus 100 nM E2. Upper traces showing EPSP pairs recorded before and 30 min after delivery of the HFS protocol. Note the lack of effect of E2 in restoring the LTP in the presence of ICI.