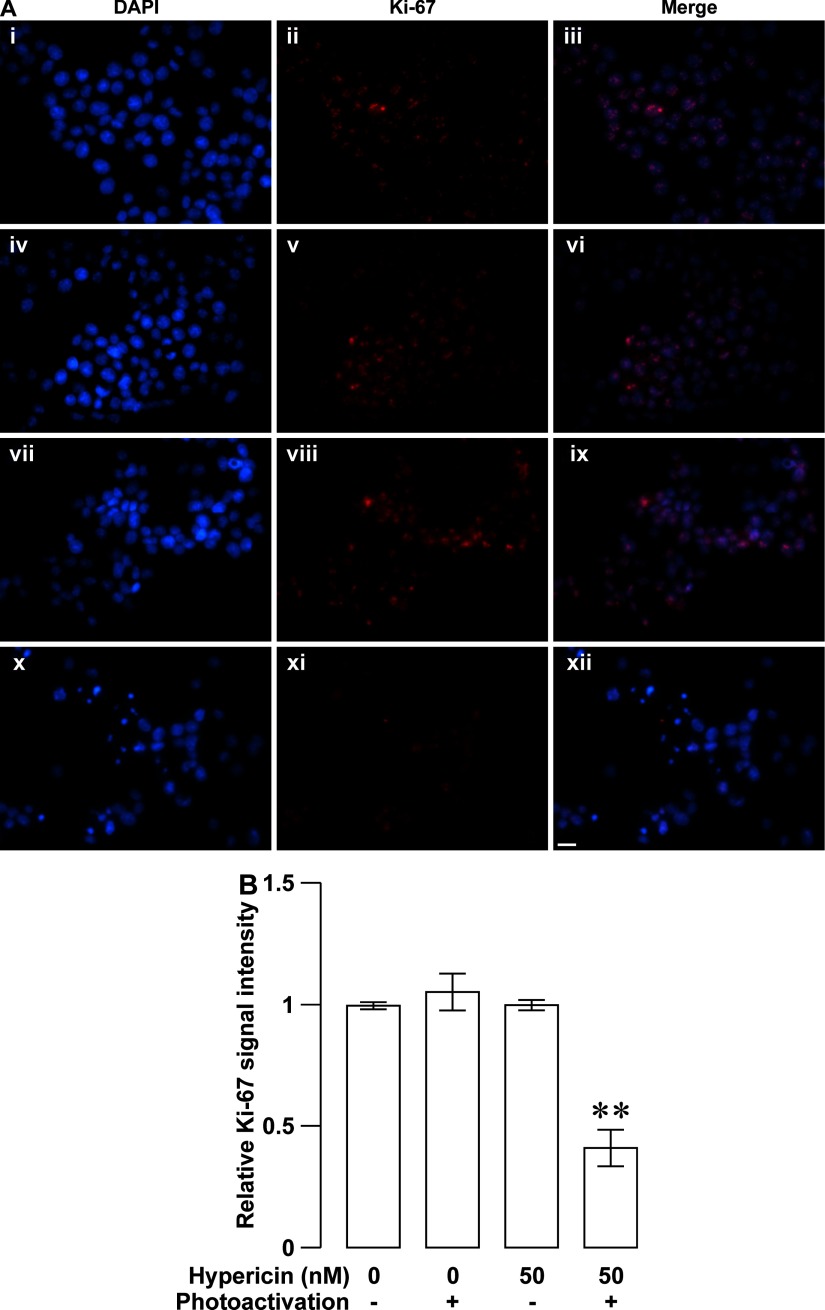
Figure 3. Photoactivated hypericin-induced down-regulation of the proliferation marker Ki-67 in RINm5F insulinoma cells.
(A) Sample Ki-67 immunofluorescence and DAPI fluorescence images were obtained in specimens subjected to solvent control treatment (control), hypericin loading (hypericin), solvent control treatment followed by photoactivation (control/photoactivation) and hypericin loading followed by photoactivation (hypericin/photoactivation). The majority of control- (ii), hypericin- (v), control/photoactivation-treated cells (viii) exhibited a similar intensity of Ki-67 immunoreactivity. A small proportion of hypericin/photoactivation-treated cells (xi) gave relatively weak Ki-67 immunoreactivity. Nuclei were verified by DAPI staining (i, iv, vii and x). Ki-67 immunoreactivity was exclusively visualized in nuclei marked with bright DAPI fluorescence (iii, vi, ix and xii). (B) Quantifications of the relative intensity of Ki-67 immunoreactivity. Control (N=3), hypericin (N=3) and control/photoactivation groups (N=3) are similar in the relative intensity of Ki-67 immunoreactivity. Hypericin/photoactivation group (N=3) showed a significant reduction in the relative intensity of Ki-67 immunoreactivity compared with the other three groups. **P<0.01 compared with control, control/photoactivation and hypericin. Bar=20 μm.