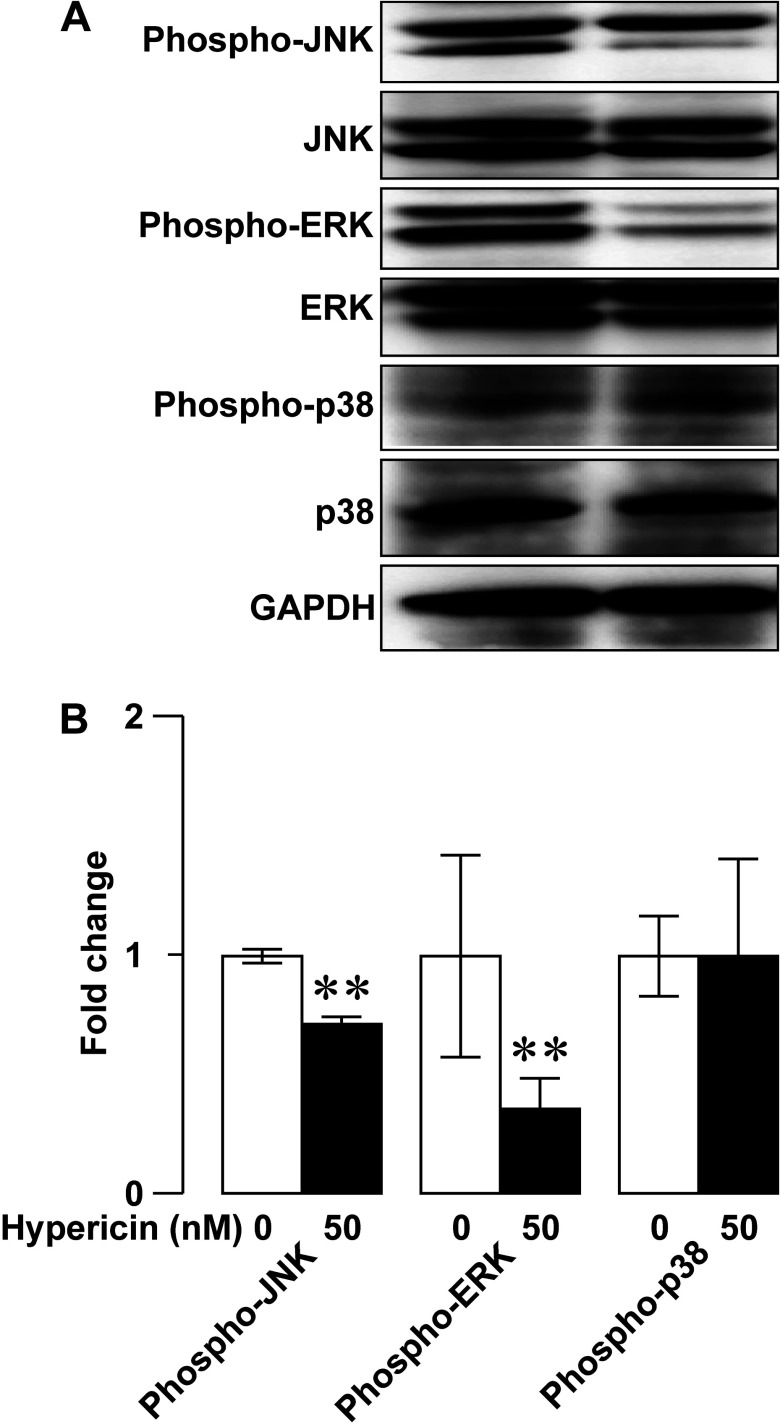
Figure 5. Photoactivated hypericin-induced decrease in the MAPKs phospho-JNK and phospho-ERK in RINm5F insulinoma cells.
(A) Representative immunoblots of cell lysates subjected to solvent control treatment followed by photoactivation (control/photoactivation; left) or hypericin loading followed by photoactivation (hypericin/photoactivation; right). JNK, ERK, phospho-p38, p38 and GAPDH immunoreactive bands in a control/photoactivation-treated sample (left) are similar to corresponding immunoreactive bands in a sample subjected to hypericin/photoactivation (right). Phospho-JNK and phospho-ERK immunoreactive bands in the hypericin/photoactivation-treated sample (right) are weaker than those in the sample subjected to control/photoactivation (left). (B) Quantifications of phospho-JNK, phospho-ERK and phosphor-p38 immunoreactive bands in control/photoactivation and hypericin/photoactivation groups. The relative abundance of phospho-JNK and phospho-ERK in hypericin/photoactivation group (N=3) significantly decreased as compared with control/photoactivation group (N=3). The relative abundance of phospho-p38 in hypericin/photoactivation group did not significantly differ from that in control/photoactivation group (N=3). **P<0.01 compared with control/photoactivation.